ISO 9001 2015 requirements, quality management systems
14/08/2017
Quiz requirements ISO 9001 version 2015 You want to familiarize yourself with the structure of the standard, identify and understand the requirements of ISO 9001 version 2015, then it's up to you to play!
The "ISO 9001 version 2015 Requirements" quiz will help you understand the main requirements of the standard.
The questions (requirements) included in this quiz are 60 of the 309 in the standard, but don't worry. These 60 requirements are among the most important. So do not hesitate to learn in a fun way!
Do not think you can finish this quiz in less than an hour, unless of course you are a little genius!
News about the ISO 9001 version 2015
The online training (course) T 15v15 ISO 9001 version 2015 readiness and its demo
The course T 35v15 ISO 9001 version 2015 internal audit and its demo
The package of courses T 65v15 training package ISO 9001 version 2015 readiness and internal audit
Based on the ISO 9001: 2015 the 309 requirements (verb shall) of clauses 4 to 10 are as follows:
|
ISO 9001 : 2015 requirements
|
||||
|
No
|
Clause
|
PDCA cycle
|
Requirement No
|
Quantity
|
|
4
|
Context of the organization | Plan | 1 ÷ 24 | 24 |
|
5
|
Leadership | Plan, Do, Check, Act |
25 ÷ 50
|
26
|
|
6
|
Planning | Plan |
51 ÷ 77
|
27
|
|
7
|
Support | Do |
78 ÷ 120
|
43
|
|
8
|
Operation | Do |
121 ÷ 248
|
128
|
|
9
|
Performance evaluation | Check |
249 ÷ 291
|
43
|
|
10
|
Improvement | Act |
291 ÷ 309
|
18
|
|
Total
|
309
|
|||
.jpg)
ISO 9001 2015 requirements
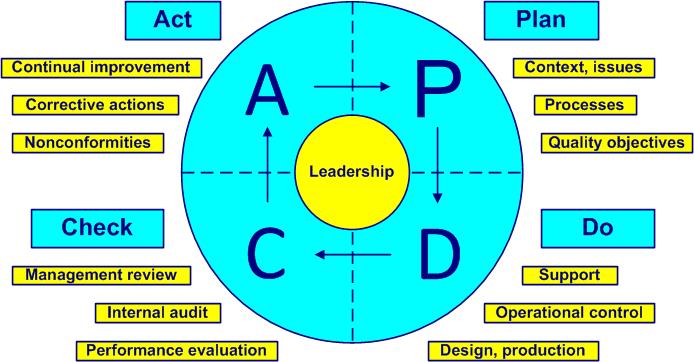
The Deming PDCA cycle
Remark. Any requirement normally begins with "The organization shall...". For simplicity's sake we present the requirements directly, starting with the verb.
|
No
|
Clause, sub-clause
|
Requirement
|
Comment, link
|
|
| 4 |
Context of the organization
|
|||
| 4.1 |
The organization and its context
|
|
||
|
4.1
|
Determine external and internal issues | Understand everything that can influence the purpose and strategic direction of the company (corporate culture, innovation, strategic direction, competition, market, compliance obligation) | ||
| 2 | 4.1 | Monitor and review information about issues | Issue: what one can gain or lose during an activity (factors, conditions) | |
| 4.2 |
Needs and expectations of interested parties
|
|
||
| 4.2 a | Identify the interested parties | "There is only one valid definition of a business purpose: to create a customer". Peter Drucker. List of relevant interested parties | ||
| 4 |
4.2 b
|
Clarify the requirements of interested parties | Each need and expectation is unique. Aim for a partnership in the long term | |
|
5
|
4.2
|
Monitor and review information about interested parties and their requirements | Before accepting an order | |
| 4.3 |
Scope of the quality management system
|
|
||
|
6
|
4.3
|
Define the scope of the QMS | Geographic and organizational scope available to interested parties | |
|
7
|
4.3 a
|
Take into account the external and internal issues | Cf. sub-clause 4.1 | |
|
8
|
4.3 b
|
Take into account the requirements of interested parties | Cf. sub-clause 4.2 | |
|
9
|
4.3 c
|
Take into account the products and services | All products and services proposed by the company without exception | |
| 10 |
4.3
|
Apply any requirement of the ISO 9001 standard applicable within the scope of the QMS | The requirements of the standard become internal requirements | |
| 11 | 4.3 | Maintain the scope of the QMS as documented information | Cf. sub-clause 7.5. Include all products and services | |
|
4.3
|
Include in the scope of the QMS justification for any requirements which cannot be met | Every requirement of the ISO 9001 standard which cannot be applied in the company implies a justification | ||
| 4.4 |
Quality management system and its processes
|
|||
|
13
|
4.4.1
|
Establish, implement, maintain and improve a process-based QMS | The company is free to decide how to apply the QMS without forgetting the issues (see sub-clause 4.1) and requirements (see sub-clause 4.2) | |
| 14 | 4.4.1 | Determine the needed processes and their application | "If you cannot describe what you are doing as a process, you do not know what you're doing". Edwards Deming. Process map | |
|
15
|
4.4.1 a
|
Determine process inputs and outputs | Process sheet | |
| 16 | 4.4.1 b | Determine the sequence and interaction of processes | Flowchart | |
| 17 | 4.4.1 c | Determine the criteria and methods to control processes | Tools of the quality manager | |
| 18 | 4.4.1 d | Determine and ensure the resources | Needed to support processes. Cf. sub-clause 7.1 | |
| 19 | 4.4.1 e | Assign process responsibilities and authorities | Job description of process owners | |
| 20 | 4.4.1 f | Take into account the risks and opportunities for each process | Plan and implement actions to address these risks, cf. sub-clause 6.1 | |
| 21 | 4.4.1 g | Evaluate processes and if necessary modify them | Identify methods to monitor, measure, check and modify processes. Cf. sub-clause 9.1.1 | |
| 22 | 4.4.1 h | Determine the improvement opportunities of processes and the QMS | Cf. sub-clause 10.1 | |
|
23
|
4.4.2
|
Maintain documented information on process operation | Cf. sub-clause 7.5. The bare essential is sufficient. Use process map | |
|
24
|
4.4.2
|
Retain documented information on process operation | Cf. sub-clause 7.5. The goal is to ensure that processes' results are those planned | |
| 5 |
Leadership
|
|||
| 5.1 |
Leadership and commitment
|
|||
|
|
5.1.1 |
General
|
|
|
|
25
|
5.1.1 a
|
Assume responsibility for the effectiveness of the QMS | "When you sweep the stairs, you start at the top". Romanian proverb. Top management demonstrates leadership (assumes its responsibility and commitment). Focus on quality and customers | |
| 26 | 5.1.1 b | Establish a quality policy and quality objectives | The policy and the objectives are compatible with strategic direction and context of the company | |
|
27
|
5.1.1 c
|
Integrate QMS requirements in the internal process requirements | Cf. sub-clause 4.4 and sub-clause 7.1.4 | |
|
28
|
5.1.1 d
|
Raise awareness of the process approach and risk-based approach | Cf. sub-clause 0.3 (introduction) and sub-clause 6.1 | |
|
29
|
5.1.1 e
|
Provide the necessary resources for the QMS | Cf. sub-clause 7.1 | |
|
30
|
5.1.1 f
|
Raise awareness on the importance of an effective and conforming QMS | Third quality management principle (engagement of people) | |
|
31
|
5.1.1 g
|
Ensure the achievement of intended results of the QMS | Essential commitment of top management | |
|
32
|
5.1.1 h
|
Support the staff contribution to the effectiveness of the QMS | "Employees first, customers second". Vineet Nayar | |
|
33
|
5.1.1 i
|
Promote continual improvement | Cf. sub-clause 10.3 | |
|
34
|
5.1.1 j
|
Support the leadership of managers | Responsibility and authority of managers are backed at all times by top management | |
|
|
5.1.2
|
Customer focus
|
||
|
35
|
5.1.2 a
|
Determine and meet customer, statutory and regulatory requirements | Top management demonstrates leadership (assumes its responsibility and commitment) permanently | |
|
36
|
5.1.2 b
|
Determine and address the potential risks and opportunities | Any risk and opportunity that may influence the conformity of products and services and customer satisfaction. Preserving the goal to always provide compliant products and services | |
|
37
|
5.1.2 c
|
Maintain the objective of better satisfying the customer | First quality management principle (customer focus) | |
| 5.2 |
Policy
|
|
||
| 5.2.1 |
Establishing the quality policy
|
|
||
|
38
|
5.2.1 a
|
Establish, implement and maintain a suitable quality policy | Top management applies a policy adapted to the purpose, strategic direction, culture and business context | |
| 39 | 5.2.1 b | Provide a framework to define and review the quality objectives | Cf. sub-clause 6.2 | |
| 40 | 5.2.1 c | Include meeting the applicable requirements | Cf. sub-clause 9.1.3 | |
| 41 | 5.2.1 d | Include a commitment to continuously improve the QMS | Cf. sub-clause 10.3 | |
| 5.2.2 |
Communicating the quality policy
|
|
||
| 42 | 5.2.2 a | Maintain the quality policy as documented information | And make it available inside the company. Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 43 | 5.2.2 b | Communicate the quality policy | So it is understand and applied, cf. sub-clause 7.4 | |
| 44 | 5.2.2 c | Keep the quality policy available | The quality policy cannot be a confidential document, it is available to relevant interested parties | |
|
5.3
|
Roles, responsibilities, authorities
|
|||
|
45
|
5.3
|
Define and communicate the responsibilities and authorities | Top management assigns all relevant roles in the QMS | |
|
46
|
5.3 a
|
Define and communicate the responsibilities and authorities | Top management assigns all relevant roles according to the requirements of the ISO 9001 standard | |
|
47
|
5.3 b
|
Define and communicate the responsibilities and authorities | Top management assigns all relevant roles so that processes deliver expected results | |
|
48
|
5.3 c
|
Define and communicate the responsibilities and authorities | Top management assigns all relevant roles so that reporting on the performance of the QMS and improvement opportunities is done, cf. sub-clause 10.1 | |
|
49
|
5.3 d
|
Define and communicate the responsibilities and authorities | Top management assigns all relevant roles so that customer focus is ensured (first quality management principle) | |
|
50
|
5.3 e
|
Define and communicate the responsibilities and authorities | Top management assigns all relevant roles so that implemented changes to the QMS do not affect its integrity | |
|
6
|
Planning
|
|||
| 6.1 |
Actions to address risks and opportunities
|
|
||
| 51 |
6.1.1 a
|
Take into account risks and opportunities | In order to ensure that the QMS can achieve its expected results, cf. sub-clauses 4.1 (context) and 4.2 (interested parties). "Any decision involves a risk". Peter Barge | |
| 52 | 6.1.1 b | Take into account opportunities | In order to increase the desirable effects (positive impact) | |
|
53
|
6.1.1 c
|
Take into account risks | In order to reduce the undesirable effects (negative impacts) | |
| 54 | 6.1.1 d | Take into account risks and opportunities | In order to confirm the approach of continual improvement, cf. sub-clause 10.3 | |
| 55 | 6.1.2 a | Plan actions to address risks and opportunities | Take into account risks in every process | |
| 56 | 6.1.2 b 1 | Plan the way to implement actions | Define how to integrate actions in the QMS processes, cf. sub-clause 4.4 | |
| 57 | 6.1.2 b 2 | Plan the way to evaluate actions | Follow the results of each action | |
| 58 | 6.1.2 | Adapt actions to risks and opportunities | Compared to the potential impact on the conformity of products and services | |
|
6.2
|
Quality objectives
|
|
||
|
59
|
6.2.1
|
Establish quality objectives for processes | "He who has no goals will not achieve them". Sun Tzu" | |
| 60 | 6.2.1 a | Choose quality objectives | Clarify criteria for setting objectives that are consistent with the quality policy | |
|
61
|
6.2.1 b
|
Use measurable objectives | And realistic | |
|
62
|
6.2.1 c
|
Consider applicable requirements | Cf. sub-clause 4.2 | |
| 63 | 6.2.1 d | Adopt relevant objectives | In order to ensure the conformity of products and services and improved customer satisfaction | |
| 64 | 6.2.1 e | Monitor objectives | Frequently | |
|
65
|
6.2.1 f
|
Communicate on objectives | At all levels | |
| 66 | 6.2.1 g | Update objectives | During management review, cf. sub-clause 9.3 | |
| 67 |
6.2.1
|
Maintain documented information on the quality objectives | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 68 |
6.2.2 a
|
Plan how to do | In order to achieve quality objectives | |
| 69 |
6.2.2 b
|
Plan necessary resources | In order to achieve quality objectives | |
| 70 |
6.2.2 c
|
Plan responsibilities | In order to achieve quality objectives | |
| 71 |
6.2.2 d
|
Plan deadlines | In order to achieve quality objectives | |
| 72 |
6.2.2 e
|
Plan the way to evaluate results | In order to achieve quality objectives | |
| 6.3 |
Planning of changes
|
|||
|
73
|
6.3 | Plan the need for changes of the QMS | "The only person who likes change is a wet baby". Cf. sub-clause 4.4 | |
|
74
|
6.3 a | Plan the changes | Taking into account the purpose of the change and the possible consequences | |
|
75
|
6.3 b | Plan the changes | Taking into account the maintenance of the integrity of the QMS | |
|
76
|
6.3 c | Plan the changes | Taking into account the available resources | |
|
77
|
6.3 d | Plan the changes | Taking into account the assigned responsibilities and authorities | |
| 7 |
Support
|
|||
| 7.1 |
Resources
|
|
||
|
|
7.1.1
|
General
|
|
|
|
78
|
7.1.1 | Provide the necessary resources | In order to support the QMS | |
|
79
|
7.1.1 a | Take into account existing resources | And their capabilities and constrains | |
|
80
|
7.1.1 b | Take into account the need for the use of external providers | In order to provide necessary services not available inside the company | |
|
|
7.1.2 |
People
|
|
|
|
81
|
7.1.2 | Provide suitable people for the effective operation of the QMS and its processes | "But in the long run - and I emphasize this - no matter how good or successful you are or how clever or crafty, your business and its future are in the hands of the people you hire". Akio Morita | |
|
7.1.3
|
Infrastructure | |||
|
82
|
7.1.3 | Provide and maintain the infrastructure necessary to the functioning of processes | In order to achieve conformity of products and services. Examples: buildings, equipment, transportation, hardware, software | |
|
7.1.4
|
Process environment | |||
|
83
|
7.1.4 | Provide and maintain the suitable environment necessary to the functioning of processes | In order to achieve conformity of products and services. Examples: corporate culture, work atmosphere, temperature, ergonomics | |
| 7.1.5 |
Monitoring and measuring resources
|
|||
| 7.1.5.1 |
General
|
|
||
|
84
|
7.1.5.1 | Provide suitable monitoring and measuring resources | In order to obtain expected inspection results | |
|
85
|
7.1.5.1 a
|
Provide adequate resources to the specific inspections | To inspect is to monitor and measure. Cf. sub-clause 7.2 | |
| 86 | 7.1.5.1 b | Maintain resources | In order to ensure fitness for their purpose | |
| 87 | 7.1.5.1 | Retain documented information on the adequacy of inspection resources | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 7.1.5.2 |
Measurement traceability
|
|
||
| 88 | 7.1.5.2 a | Verify or calibrate regularly the measuring equipment | In order to have confidence in the measurement results. When no such standards exist retain documented information on the reference used, cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 89 | 7.1.5.2 b | Identify the measuring equipment | In order to monitor the validity of their calibration (or verification) | |
| 90 | 7.1.5.2 c | Protect the measuring equipment | Against activities that may invalidate the results of the measurement (settings or deterioration) | |
| 91 | 7.1.5.2 | Conduct corrective action on previous measurement results | When the verification or calibration of a measuring instrument is not in conformity | |
|
|
7.1.6
|
Organizational knowledge | ||
| 92 | 7.1.6 | Determine the necessary knowledge | In order to control the processes and the conformity of products and services | |
| 93 | 7.1.6 | Acquire, maintain and make organizational knowledge available to the extend necessary | In order to maintain the performance of the QMS | |
| 94 | 7.1.6 | Take into account the need for additional knowledge | When needs and trends have changed | |
| 7.2 |
Competence
|
|||
| 95 | 7.2 a | Determine the necessary competence | Clarify quality competence requirements. Identify people who have an influence on the quality performance | |
| 96 | 7.2 b | Ensure the competence | Which are based on appropriate training or experience | |
| 97 | 7.2 c | Undertake activities to acquire the necessary competence and evaluate the effectiveness of these activities | Training, coaching, external providers | |
| 98 | 7.2 d | Retain documented information on staff competence | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 7.3 | Awareness | |||
| 99 | 7.3 a | Ensure the staff is aware of the quality policy | Including people who carry out work under the company's control. Cf. sub-clause 5.2 | |
| 100 | 7.3 b | Ensure the staff is aware of the quality objectives | Cf. sub-clause 6.2 | |
| 101 | 7.3 c | Ensure the staff is aware of its contribution | In order to improve the performance of the QMS | |
| 102 | 7.3 d | Ensure the staff is aware of negative impacts | If QMS requirements are not met | |
| 7.4 |
Communication
|
|||
| 103 | 7.4 a | Define the subjects on which to communicate | Internally and externally. "Good news walks, bad news runs". Swedish proverb | |
| 104 | 7.4 b | Define when to communicate | Respond quickly to claims | |
| 105 | 7.4 c | Define with whom to communicate | Communication goes both ways | |
|
106
|
7.4 d
|
Define how to communicate | Orally, in writing; Internet, video | |
|
107
|
7.4 e
|
Assign who will communicate | The one who is closest to the subject | |
| 7.5 |
Documented information
|
|||
| 7.5.1 |
General
|
|||
| 108 | 7.5.1 a | Include the documented information required by the ISO 9001 standard | Documented information to maintain (documented procedures) :
|
|
| 109 | 7.5.1 b | Select the documented information deemed necessary to the effectiveness of the QMS | "Spoken words fly away, written one stay". Latin proverb | |
| 7.5.2 |
Creating and updating
|
|||
| 110 | 7.5.2 a | Create, identify and describe the documented information | Codification, title, author, subject, product | |
| 111 | 7.5.2 b | Choose the format and the media of the documented information | Language, graphics; paper, electronic | |
| 112 | 7.5.2 c | Review and approve the adequacy of the documented information | Who writes, codifies, who approves | |
| 7.5.3 |
Control of documented information
|
|||
| 113 | 7.5.3.1 a | Control the availability of the documented information | Where and when required in a form that is suitable for use | |
| 114 | 7.5.3.1 b | Control the protection of the documented information | Loss of confidentiality, loss of integrity, misuse | |
| 115 | 7.5.3.2 a | Control the distribution, access and use of the documented information | Who is in charge, method to use, rule to follow | |
| 116 | 7.5.3.2 b | Control the storage of the documented information | Including preservation, protection and readability | |
| 117 | 7.5.3.2 c | Control the changes of the documented information | Use of updated versions, restricted access to obsolete versions | |
| 118 | 7.5.3.2 d | Control the retention time and the removal of the documented information | Retention period, disposal method | |
| 119 | 7.5.3.2 | Control the documented information of external origin | Unique codification, access, protection | |
| 120 | 7.5.3.2 | Protect the documented information | Who has the right to read, who has the right to change | |
| 8 |
Operation
|
Do | ||
| 8.1 |
Operational planning and control
|
|||
| 121 | 8.1 a | Plan and determine the requirements for the products and services | By controlling processes. Cf. sub-clauses 4.4 et 6.1 | |
| 122 | 8.1 b 1 | Establish the criteria | For processes | |
| 123 | 8.1 b 2 | Establish the criteria | For the acceptance of conforming products and services | |
| 124 | 8.1 c | Determine necessary resources | Needed to achieve conformity of products and services | |
| 125 | 8.1 d | Control the processes | In accordance with the criteria of sub-clauses 8.1 b 1 and 8.1 b 2 | |
| 126 | 8.1 e 1 | Determine, maintain and retain the documented information on process control | To have confidence that the process results are as expected. Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 127 | 8.1 e 2 | Determine, maintain and retain the documented information on product and service conformity | Meet applicable requirements. Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 128 | 8.1 | Control planned and unplanned changes | Analyse the consequences of unplanned changes, actions to limit the effects | |
| 129 | 8.1 | Control the outsourced processes | Cf. sub-clause 8.4 | |
| 8.2 |
Requirements for products and services
|
|||
| 8.2.1 |
Customer communication
|
|||
| 130 | 8.2.1 a | Provide information to customers | Related to products and services | |
| 131 | 8.2.1 b | Control communication with customers | Related to contracts, orders, changes and consultations | |
| 132 | 8.2.1 c | Control communication with customers | Regarding the perception, opinions, complaints and recommendations. "The most important thing in communication is hearing what is not said". Peter Drucker | |
| 133 | 8.2.1 d | Control communication with customers | Regarding their property. Cf. sub-clause 8.5.3 | |
| 134 | 8.2.1 e | Control communication with customers | Regarding specific requirements for contingency actions | |
| 8.2.2 |
Determining the requirements related to products and services
|
|||
| 135 | 8.2.2 a 1 | Develop specific activities for products and services | In order to clarify statutory and regulatory requirements | |
| 136 | 8.2.2 a 2 | Define internal requirements | Related to processes, products and services. And check that the requirements can be met | |
| 137 | 8.2.2 b | Be able to respond to claims | In a relevant way (with facts) | |
| 8.2.3 | Review of requirements related to products and services |
|
||
| 138 | 8.2.3.1 | Be able to respond to customers | Regarding requirements of proposed products and services | |
| 139 | 8.2.3.1 a | Review explicit customer requirements | Before order acceptance. Including delivery and post-delivery activities requirements | |
| 140 | 8.2.3.1 b | Review implicit customer requirements | Before order acceptance. Unformulated requirements but necessary for specified use or use intended by the customer | |
| 141 |
8.2.3.1 c
|
Review internal requirements | Between requirements of an order and those previously expressed | |
| 142 |
8.2.3.1 d
|
Review statutory and regulatory requirements | Applicable to the products and services | |
| 143 | 8.2.3.1 e | Review gaps | Between requirements of an order (or contract) and those previously expressed | |
| 144 | 8.2.3.1 | Resolve gaps | Before order acceptance and commitment to provide products and services | |
| 145 | 8.2.3.1 | Confirm requirements before accepting an order | When requirements are not documented | |
| 146 | 8.2.3.2 a | Retain the documented information on the results of the reviews of requirements | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 147 | 8.2.3.2 b | Retain the documented information on any new or changed requirement for the products and services | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 8.2.4 | Changes to requirements for products and services |
|
||
| 148 | 8.2.4 | Communicate changes to relevant persons | After changing requirements in the documented information | |
| 8.3 |
Design and development of products and services
|
|||
| 8.3.1 |
General
|
|||
| 149 | 8.3.1 | Establish, implement and maintain a process of design and development | When the product or service requirements are not yet defined. "I have not failed. I just found 10,000 ways that will not work". Thomas Edison | |
| 8.3.2 | Design and development planning | |||
| 150 | 8.3.2 a | Plan the design and development stages | Taking into account the specificity of design and development activities | |
| 151 | 8.3.2 b | Plan the design and development stages | Taking into account the process requirements and applicable reviews | |
| 152 | 8.3.2 c | Plan the design and development stages | Taking into account the verification and validation activities | |
| 153 | 8.3.2 d | Plan the design and development stages | Taking into account the necessary responsibilities and authorities | |
| 154 | 8.3.2 e | Plan the design and development stages | Taking into account the needs of internal and external resources | |
| 155 | 8.3.2 f | Plan the design and development stages | Taking into account the relations between persons participating in the design and development | |
| 156 | 8.3.2 g | Plan the design and development stages | Taking into account the need for involvement of customers and users | |
| 157 | 8.3.2 h | Plan the design and development stages | Taking into account the requirements for subsequent products and services | |
| 158 | 8.3.2 i | Plan the design and development stages | Taking into account the level of control expected by interested parties | |
| 159 | 8.3.2 j | Plan the design and development stages | Taking into account the documented information meeting design and development requirements. Cf. sub-clauses 8.3.3, 8.3.5 and 8.3.6 | |
| 8.3.3 |
Design and development inputs
|
|||
| 160 | 8.3.3 | Determine essential requirements | On specific types of products and services from design and development | |
| 161 | 8.3.3 a | Determine functional requirements | Taking into account also the performance requirements | |
| 162 | 8.3.3 b | Clarify inputs | Taking into account the information from similar activities | |
| 163 | 8.3.3 c | Clarify inputs | Taking into account the statutory and regulatory requirements | |
| 164 | 8.3.3 d | Clarify inputs | Taking into account the corporate culture, internal rules of art | |
| 165 | 8.3.3 e | Clarify inputs | Taking into account the potential consequences of product and service failure | |
| 166 | 8.3.3 | Check that the input items are complete and unambiguous | In order to realize suitable design and development process | |
| 167 | 8.3.3 | Resolve potential conflicts between inputs | In order to obtain complete and unambiguous inputs | |
| 168 | 8.3.3 | Retain the documented information on design and development inputs | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 8.3.4 |
Design and development controls
|
|||
| 169 | 8.3.4 a | Define clearly the expected results | Regarding processes, products and services | |
| 170 | 8.3.4 b | Conduct reviews as planned | Regarding processes, products and services | |
| 171 | 8.3.4 c | Check that outputs meet input requirements | Cf. sub-clause 8.3.5 | |
| 172 | 8.3.4 d | Validate products and services | To ensure that the specified application requirements or those for the intended use are satisfied | |
| 173 | 8.3.4 e | Take actions in response to identified problems | During reviews, verifications and validations | |
| 174 | 8.3.4 f | Ensure that the documented information is retained | Cf. sub-clause 7.5. Cf. sub-clauses 8.3.3, 8.3.5 and 8.3.6 | |
| 8.3.5 | Design and development outputs |
|
||
| 175 | 8.3.5 a | Ensure that outputs meet input requirements | Cf. sub-clause 8.3.3 | |
| 176 | 8.3.5 b | Ensure that outputs are in line with the subsequent processes | Regarding the products and services | |
| 177 | 8.3.5 c | Ensure that outputs include monitoring and measuring requirements | Including acceptance criteria | |
| 178 | 8.3.5 d | Ensure that outputs are suitable for their intended use | Proper use or planned by the customer in complete safety | |
| 179 | 8.3.5 | Retain the documented information on outputs | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
|
|
8.3.6 |
Design and development changes
|
||
| 180 | 8.3.6 | Identify, review and control the changes made to inputs and outputs | To ensure that the changes have no impact on meeting the requirements | |
| 181 | 8.3.6 a | Retain the documented information on changes | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 182 | 8.3.6 b | Retain the documented information on results of reviews | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 183 | 8.3.6 c | Retain the documented information on who authorized the changes | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 184 | 8.3.6 d | Retain the documented information on actions | In order to prevent negative impacts. Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 8.4 |
External providers
|
|||
| 8.4.1 |
General
|
|||
| 185 | 8.4.1 | Ensure that the outputs of external providers meet specified requirements | "You can outsource the activity, but you cannot outsource risk". Michael Gallagher | |
| 186 | 8.4.1 a | Apply the requirements for the control of products and services provided by external providers | When the products and services are integrated internally | |
| 187 | 8.4.1 b | Apply the requirements for the control of products and services | When the products and services are provided directly to customers by external providers on behalf of the company | |
| 188 | 8.4.1 c | Apply the requirements for the control of process done by external providers | When a decision has been made to outsource the process | |
| 189 | 8.4.1 | Establish and implement evaluation and selection criteria of external providers and monitor their performance | Including regular re-evaluation | |
| 190 | 8.4.1 | Retain the documented information on the results of the evaluation and monitoring | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 8.4.2 |
Type and extent of control
|
|||
| 191 | 8.4.2 | Ensure the level of control of external providers on meeting the requirements | In order that the provision of external providers do not affect the conformity of products and services delivered to the customer | |
| 192 | 8.4.2 a | Ensure that the processes of external providers are controlled | In conformity with the external service provider QMS. Any outsourced process is included in the scope of the QMS | |
| 193 | 8.4.2 b | Define how to control the external provider and its process outputs | The level of control (or influence) of an external service provider is sometimes a very sensitive area. Stay alert and caring! | |
| 194 | 8.4.2 c 1 | Take into account the potential impact of the outputs of the external provider | On meeting the requirements of products and services delivered to the customer and on statutory and regulatory requirements | |
| 195 | 8.4.2 c 2 | Take into account the control of the external provider | And effectiveness of this control | |
| 196 | 8.4.2 d | Define how to control the outputs of externally provided processes | Verification and other activities necessary to ensure that the provision of external providers does not affect the conformity of products and services delivered to the customer | |
| 8.4.3 |
Information for external providers
|
|||
| 197 | 8.4.3 | Check the adequacy of the requirements | And only after communicate them to the external provider | |
| 198 | 8.4.3 a | Communicate the requirements to the external provider | Regarding the processes, products and services to provide | |
| 199 | 8.4.3 b 1 | Communicate the requirements to the external provider | Regarding the approval of products and services | |
| 200 | 8.4.3 b 2 | Communicate the requirements to the external provider | Regarding the approval of methods, processes and equipment | |
| 201 | 8.4.3 b 3 | Communicate the requirements to the external provider | Regarding the approval of the release of products and services | |
| 202 | 8.4.3 c | Communicate the requirements to the external provider | Regarding the competence (including required qualifications) | |
| 203 | 8.4.3 d | Communicate the requirements to the external provider | Regarding the relations between the external provider and the company | |
| 204 | 8.4.3 e | Communicate the requirements to the external provider | Regarding the control and monitoring of the external provider's performance | |
| 205 | 8.4.3 f | Communicate the requirements to the external provider | Regarding the verification or validation activities that the company or its customer intends to realize at the external provider's premises | |
| 8.5 |
Production and service provision
|
|||
| 8.5.1 |
Control of production and service provision
|
|||
| 206 | 8.5.1 | Apply controlled conditions of production and service provision | Including delivery and post-delivery activities | |
| 207 | 8.5.1 a 1 | Save documented information of specifications of products and services and the expected activities | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 208 | 8.5.1 a 2 | Save the documented information of results to be achieved | Cf. sub-clause 7.5. "A quality control that does not show results is no control". Kaoru Ishikawa | |
| 209 | 8.5.1 b | Include in the controlled conditions the inspection resources | Cf. sub-clause 7.1.5 | |
| 210 | 8.5.1 c | Include in the controlled conditions the inspection activities | To verify that the appropriate stages of the processes' outputs meet the criteria | |
| 211 | 8.5.1 d | Include in the controlled conditions adequate infrastructure and environment | Cf. sub-clauses 7.1.3 et 7.1.4 | |
| 212 | 8.5.1 e | Include in the controlled conditions the staff competence | Including the necessary qualification, cf. sub-clause 7.2 | |
| 213 | 8.5.1 f | Include in the controlled conditions the validation of the ability of a process to achieve the expected results | Only in the case when the outputs cannot be checked a posteriori | |
| 214 | 8.5.1 g | Include in the controlled conditions the actions to prevent human error | Use tools such as Poka-Yoke | |
| 215 | 8.5.1 h | Include in the controlled conditions the activities of release, delivery and post-delivery | Cf. sub-clause 8.6 and sub-clause 8.5.5 | |
| 8.5.2 |
Identification and traceability
|
|||
| 216 | 8.5.2 | Use appropriate means to control the unique identification of process outputs | In order to ensure the conformity of products and services when needed | |
| 217 | 8.5.2 | Inspect processes throughout the production and service provision | In order to identify the status of process outputs | |
| 218 | 8.5.2 | Control the traceability of process outputs | When traceability is a requirement, the unique identification is used | |
| 219 | 8.5.2 | Retain the documented information on traceability | Cf. sub-clause 7.5. When traceability is a requirement, the unique identification of outputs is used | |
| 8.5.3 |
Property belonging to customers or external providers
|
|||
| 220 | 8.5.3 | Exercise care with property owned by customer or external provider | During its use or protection | |
| 221 | 8.5.3 | Identify, check, protect, monitor and safeguard customer or external provider property | When used or incorporated with updated labels | |
| 222 | 8.5.3 | Notify the customer or external provider when his property has been damaged or lost and maintain the documented information on the situation | Following incorrect or improper use. Cf. sub-clause 7.5. | |
| 8.5.4 |
Preservation
|
|||
| 223 | 8.5.4 | Preserve the process outputs throughout production and service provision activities | Some examples of preservation methods: identification, packaging, handling, storage, transport, protection | |
| 8.5.5 |
Post-delivery activities
|
|||
| 224 | 8.5.5 | Meet the requirements for post-delivery activities | Examples of post-delivery activities: exchange new product, maintenance, recycling, final disposal | |
| 225 | 8.5.5 a | Take into account statutory and regulatory requirements | Cf. sub-clause 4.2 | |
| 226 | 8.5.5 b | Take into account negative impacts related to products and services | These are consequences of potential risks | |
| 227 | 8.5.5 c | Take into account the nature, the intended use and lifetime of products and services | When the extent of post-delivery activities has been clarified | |
| 228 | 8.5.5 d | Take into account the requirements of interested parties | And customers especially | |
| 229 | 8.5.5 e | Take into account customer feedback | Of interested parties, when the extent of post-delivery activities has been clarified | |
| 8.5.6 |
Control of changes
|
|||
| 230 | 8.5.6 | Review and control unplanned changes | Cf. sub-clause 6.3 (planned changes) | |
| 231 | 8.5.6 | Retain the documented information on unplanned changes | Cf. sub-clause 7.5. Include the results of reviews, the authorization of changes and actions implemented | |
| 8.6 |
Release of products and services
|
|||
| 232 | 8.6 | Check products and services with activities at appropiate stages | "Inspection does not improve quality, nor guarantee quality". Edwards Deming | |
| 233 | 8.6 | Release products and services after verification of conformity | Unless written approval (concession) by a competent authority or client | |
| 234 | 8.6 | Retain the documented information on the release of products and services | Cf. sub-clause 7.5. | |
| 235 | 8.6 a | Include in the documented information evidence of conformity | These are the results of inspections compared to the acceptance criteria | |
| 236 | 8.6 b | Include in the documented information the traceability of products and services | Including the person having authorized the release | |
| 8.7 |
Control of nonconforming outputs
|
|||
| 237 | 8.7.1 | Identify and treat nonconforming process, products and services outputs | Marking and isolation to prevent unintended use or mixing with conforming outputs | |
| 238 | 8.7.1 | Carry out corrective actions commensurate to impacts | Including after delivery. Cf. sub-clause 10.2 | |
| 239 | 8.7.1 | Carry out corrective actions on post-delivery activities | Cf. sub-clause 8.5.5 | |
| 240 | 8.7.1 a | Handle nonconforming outputs with corrections | Repeat work, retouching, repair, recycling | |
| 241 | 8.7.1 b | Handle nonconforming outputs by segregation | Including customer returns or products and services not released | |
| 242 | 8.7.1 c | Inform the customer | Cf. sub-clause 7.4 | |
| 243 | 8.7.1 d | Handle nonconforming outputs by asking authorization | To use in is (acceptance under concession) | |
| 244 | 8.7.1 | Check conformity after any correction | After any correction go through the normal flow | |
| 245 | 8.7.2 a | Retain the documented information on the description of nonconformities | Cf. sub-clause 7.5. | |
| 246 | 8.7.2 b | Retain the documented information on implemented actions | Cf. sub-clause 7.5. | |
| 247 | 8.7.2 c | Retain the documented information on approved concessions | Cf. sub-clause 7.5. | |
| 248 | 8.7.2 d | Retain the documented information on the person having decided the handling of the nonconformities | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 9 |
Performance evaluation
|
Check | ||
| 9.1 |
Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation
|
|||
| 9.1.1 |
General
|
|||
| 249 | 9.1.1 a | Determine what is necessary to inspect | "If you can’t measure it, you can’t manage it". Peter Drucker | |
| 250 | 9.1.1 b | Determine the methods for inspection, analysis and evaluation | In order to ensure valid results | |
| 251 | 9.1.1 c | Determine when to inspect | At key stages (essential) or upon the customer's request | |
| 252 | 9.1.1 d | Determine when to analyse and evaluate inspection results | When that brings added value | |
| 253 | 9.1.1 | Evaluate the performance and effectiveness of the QMS | In order to ensure that specified requirements are met | |
| 254 | 9.1.1 | Retain the documented information on the inspection results | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 9.1.2 |
Customer satisfaction
|
|||
| 255 | 9.1.2 | Regularly monitor customer perception about their level of satisfaction | "The only measure of quality is customer satisfaction" | |
| 256 | 9.1.2 | Determine methods for obtaining and using customer information | Satisfaction surveys, claims, customer returns, recommendations | |
| 9.1.3 |
Analysis and evaluation
|
|||
| 257 | 9.1.3 | Analyse and evaluate inspection data | "Get the facts, analyze them and then do what seems right". Robert Waterman | |
| 258 | 9.1.3 a | Use analysis results | In order to evaluate how requirements are met. Cf. sub-clause 4.2 | |
| 259 | 9.1.3 b | Use analysis results | In order to evaluate the level of customer satisfaction. Cf. sub-clause 9.1.2 | |
| 260 | 9.1.3 c | Use analysis results | In order to evaluate the performance and effectiveness of the QMS | |
| 261 | 9.1.3 d | Use analysis results | In order to evaluate the effectiveness of planning. Cf. sub-clause 8.1 | |
| 262 | 9.1.3 e | Use analysis results | In order to evaluate the effectiveness of actions implemented to address risks and opportunities. Cf. sub-clause 6.1 | |
| 263 | 9.1.3 f | Use analysis results | In order to evaluate the performance of external providers. Cf. sub-clause 8.4 | |
| 264 | 9.1.3 g | Use analysis results | In order to evaluate the improvement opportunities of the QMS. Cf. sub-clause 10.3 | |
| 9.2 |
Internal audit
|
|||
| 265 | 9.2.1 a 1 | Conduct regularly planned internal audits | In order to determine whether the QMS meets internal company requirements. Cf. ISO 19011 | |
| 266 | 9.2.1 a 2 | Conduct regularly planned internal audits | In order to determine whether the QMS meets requirements of the ISO 9001 standard | |
| 267 | 9.2.1 b | Conduct regularly planned internal audits | In order to determine whether the QMS is effectively implemented and maintained | |
| 268 | 9.2.2 a | Plan, establish, implement and update an audit programme | Include the frequency, methods, responsibilities, planning requirements (audit programme) and reporting requirements (audit report) | |
| 269 | 9.2.2 a | Take into account in the audit programme essential points | Essentials points :
|
|
| 270 | 9.2.2 b | Define the scope and audit criteria | Limit the area to be audited; use specific and known by the auditee criteria | |
| 271 | 9.2.2 c | Select auditors | Do not audit your department. "No one is judge in his own case". Latin proverb | |
| 272 | 9.2.2 d | Communicate audit results to management concerned | Cf. sub-clause 7.4 | |
| 273 | 9.2.2 e | Undertake a correction quickly and corrective actions if necessary | Cf. sub-clause 10.2 | |
| 274 | 9.2.2 f | Retain the documented information on the audit programme and the audit reports | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 9.3 |
Management review
|
|||
| 9.3.1 |
General
|
|||
| 275 | 9.3.1 | Proceed at least once a year to review the QMS | In order to confirm that it is still relevant, appropriate and effective. "No system is perfect" | |
| 9.3.2 |
Management review inputs
|
|
||
| 276 | 9.3.2 a | Plan and carry out the management review | Regarding the status of actions of the previous review | |
| 277 | 9.3.2 b | Carry out the management review taking into account the changes of external and internal issues for the QMS | Including strategic direction | |
| 278 | 9.3.2 c 1 | Take into account the information on the performance of the QMS and trends | Customer satisfaction, feedback. Cf. sub-clauses 8.7 et 10.2 | |
| 279 | 9.3.2 c 2 | Take into account the information on the performance of the QMS and trends | The achievement of quality objectives, cf. sub-clause 6.2 | |
| 280 | 9.3.2 c 3 | Take into account the information on the performance of the QMS and trends | Process performance and conformity of outputs. Cf. sub-clause 9.1 | |
| 281 | 9.3.2 c 4 | Take into account the information on the performance of the QMS and trends | Nonconformities and corrective actions. Cf. sub-clause 10.2 | |
| 282 | 9.3.2 c 5 | Take into account the information on the performance of the QMS and trends | Inspection results. Cf. sub-clause 9.1 | |
| 283 | 9.3.2 c 6 | Take into account the information on the performance of the QMS and trends | Audit results. Cf. sub-clause 9.2 | |
| 284 | 9.3.2 c 7 | Take into account the information on the performance of the QMS and trends | Performance of external providers. Cf. sub-clause 8.4 | |
| 285 | 9.3.2 d | Take into account resources | Availability of resources. Cf. sub-clause 7.1 | |
| 286 | 9.3.2 e | Take into account the effectiveness of actions | Implemented to address risks and opportunities. Cf. sub-clause 6.1 | |
| 287 | 9.3.2 f | Take into account improvement opportunities | Continual improvement. Cf. sub-clause 10.3 | |
| 9.3.3 |
Management review outputs
|
|||
| 288 | 9.3.3 a | Include decisions regarding opportunities for continual improvement in the outputs of the management review | Cf. sub-clause 10.3 | |
| 289 | 9.3.3 b | Include decisions regarding eventual changes to the QMS in the outputs of the management review | Cf. sub-clause 6.3 | |
| 290 | 9.3.3 c | Include decisions regarding new resource needs in the outputs of the management review | Cf. sub-clause 7.1 | |
| 291 | 9.3.3 | Retain the documented information on outputs of the review of management | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 10 |
Improvement
|
Act | ||
| 10.1 |
General
|
|||
| 292 | 10.1 | Find improvement opportunities and implement necessary actions | In order to enhance customer satisfaction. "Where there is a problem, there is potential for improvement". Masaaki Imai | |
| 293 | 10.1 a | Improve products and services | Support innovation. In order to better meet current requirements and anticipate future requirements | |
| 294 | 10.1 b | Reduce negative impacts | Implementing corrective actions and global prevention (efficient QMS) | |
| 295 | 10.1 c | Improve the results of the QMS | To achieve the objectives of the QMS regarding performance | |
| 10.2 |
Nonconformity and corrective action
|
|||
| 296 | 10.2.1 a 1 | React to the nonconformity | In order to reduce costs. Including all claims by processing, controlling, correcting. "One of the best ways to measure quality is to calculate the price of nonconformities". Philip Crosby | |
| 297 | 10.2.1 a 2 | Take into account consequences | Think risk-based approach | |
| 298 | 10.2.1 b 1 | Examine the nonconformity | And if necessary decide to carry out a corrective action | |
| 299 | 10.2.1 b 2 | Investigate root causes | So that the nonconformity does not happen again | |
| 300 | 10.2.1 b 3 | Search for similar nonconformities | In order to apply the same recipe (why reinvent the wheel?) | |
| 301 | 10.2.1 c | Implement the necessary corrective actions | In order to treat the nonconformity | |
| 302 | 10.2.1 d | Review the effectiveness of any implemented corrective action | In order to check whether the action is finalized | |
| 303 | 10.2.1 e | Update risks and opportunities | If necessary | |
| 304 | 10.2.1 f | Make changes to the QMS | If necessary | |
| 305 | 10.2.1 | Respond proportionally to nonconformities consequences | Do not make too much quality | |
| 306 | 10.2.2 a | Retain documented information on the nature of nonconformities | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 307 | 10.2.2 a | Retain documented information on results of implemented actions | Cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 10.3 |
Continual improvement
|
|||
| 308 | 10.3 | Improve continually the performance of the QMS | In order to find improvement opportunities | |
| 309 | 10.3 | Take into account the outputs of the analysis, evaluation and management review | Cf. sub-clause 9.1.3 and sub-clause 9.3 | |




