1 OH&S approach
1.1 Background
Occupational health and safety standards' evolution
Other OH&S proverbs and quotes
.jpg)
The first laws on health and safety at work emerged in France in the late nineteenth century.
According to the International Labour Organization (the tripartite UN agency to promote decent work throughout the world) there are approximately 270 million occupational accidents each year and 160 million cases of occupational diseases in the world. The concept of decent work implies safe work that leads to the economic well-being of people.
The first Labor Code was promulgated in France in 1910.
One proven way to protect workers is to establish an occupational health and safety (OH&Soccupational health and safety) management system.
For France, the integration of occupational risk assessment (related to health and safety of workers) in the management of each organizationa structure that satisfies a need (see also ISO 9000, 3.3.1) has been an obligation of the Labour Code (R4121-1) since 2001.
The structure of the ISO 45001 standard is based on Annex SL of the ISO/IEC directives, Part 1, consolidated ISO Supplement in 2014. This is the same structure used for the new versions of ISO 9001 and ISO 14001. This facilitates the process of an integrated QSEquality, safety, environment (Quality, Safety and Environment) management system.
1.2 Scope
Scope of the OH&SMS, certification
.jpg)
The ISO 45001 standard is generic because it applies to the management system of any organization, without any constraints on the size, activity or type. It is an international voluntary standard that allows certification by an accredited body.
To achieve certification, the occupational health and safety management system (OH&SMS) must be:
- determined
- implemented
- maintained
- improved and
- compliant with
- developed OH&S policy
- requirements of the ISO 45001 standard
1.3 Steps
Preparation, implementation, benefits, Deming cycle
A well-prepared approach is halfway to success
The approach to implementing an OH&Soccupational health and safety management system goes through several steps. An example of preparation is shown in figure 1-1.
.jpg)
Figure 1-1. OH&SMS preparation
Step one contains the determination of the needs and expectations (requirementsexplicit or implicit need or expectation (see also ISO 9000, 3.1.2)) of interested parties (internal and external). The involvement of top management at its highest level is truly indispensable. The advice of a consultant is often solicited. Determing the current status of the management system (or what exists of it) would be welcome at this stage. An external certification body is chosen.
One of the key questions that comes up quickly (step 2) is the need for this decision. If this is not really necessary or if the estimated costs of the certification approach exceed the available resources, it is better to give up the idea right now.
The benefits of implementing and certificating an OH&Soccupational health and safety management system are often:
- improved image of the organization
- reinforced worker safety
- reduced or eliminated incidents
- increased confidence of interested parties
- reduced production costs
- reduced insurance costs
- better preparation for emergencies
- the prevention of hazards becoming routine
- workers that are aware, consulted, motivated and proud
- high level of risk control
- good practices valorised
- commitment profitable for all
- up-to-date legal OH&S obligations
More than one and a half million businesses worldwide can not be wrong!
IBM, one of the world leaders in information technology, has implemented ISO 45001 to improve the management of stress and psychosocial risks at work. Implementing prevention and support measures for employees has helped reduce stress and improve well-being at work.
IBM has recorded a significant improvement in the mental health of its employees, demonstrating the importance of addressing psychosocial risks and the company's commitment to the well-being of its employees
The internalization of the spirit of the principles and requirementsexplicit or implicit need or expectation (see also ISO 9000, 3.1.2) of an ISO standard significantly improves the overall performance of your business, especially when it is not considered as a constraint.
The third step shall determine whether this approach receives the approval of workers. A communication campaign is launched in-house on the objectives of an OH&S management system (OH&SMS). Workers are aware and understand that, without their participation, the project cannot succeed.
Have confidence: success will come with the involvement and effort of all!
The vision (what we want to be), the mission (why we exist) and the business plan of the organization are set. The next step (4) begins with a preliminary analysis of legal and regulatory requirements and continues wit the establishment of an outline of the OH&S policy and OH&S objectives. If you do not have a copy of the ISO 45001 standard, now is the time to get it (cf. § 2.1 of the present course).
Planning is the last step (5) of the project preparation for obtaining ISO 45001 certification. A reasonable period is between 5 to 8 months (each organization is unique and specific). A managementrepresentative is appointed as project leader. Top management commitment is formalized in a document communicated to all staff.
The establishment and implementation of an ISO 45001 OH&Soccupational health and safety management system are shown in figure 1-2.
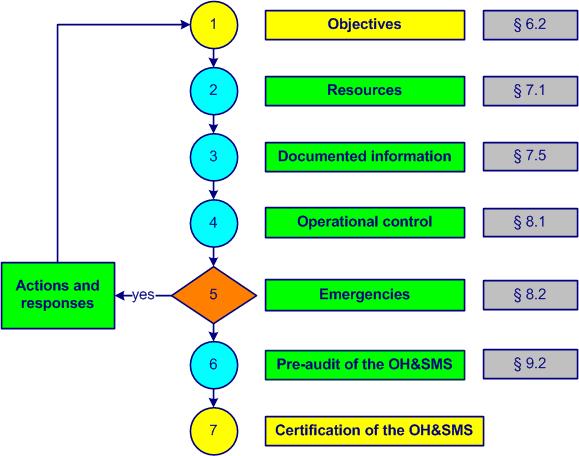
Figure 1-2. QMS implementation
Internal audits allow evaluation of the degree of system implementation (hazard identification, risk assessment, legal and other requirementsexplicit or implicit need or expectation (see also ISO 9000, 3.1.2)). This step (1) makes it possible to define the objectives.
In step 2 the resources to achieve the OH&Soccupational health and safety objectives are set. Planning tasks, responsibilities and time frames are established. Workers are aware of potential hazards. Training of internal auditors is taken into account.
Step 3 allows you to establish early versions of documented information related to the OH&Soccupational health and safety management system with the participation of the maximum number of available persons.
Operational control happens in step 4. The activities associated with identified hazards are planned and implemented. Internal and external communications are established and formalized. A legal watch is developed. A management review is recommended.
Emergency situations with potential impacts on occupational health and safety are listed in step 5. The responses (action and reaction) to emergencies are implemented and documented.
To conduct the pre-audit of the OH&SMS (step 6), documents such as the OH&Soccupational health and safety manual, procedures and others are checked and approved by the competent authorities. A management review evaluates whether applicable requirementsexplicit or implicit need or expectation (see also ISO 9000, 3.1.2) are met. The OH&Soccupational health and safety policy and objectives are finalized. An OH&Soccupational health and safety manager from another organization or a consultant can provide valuable feedback, suggestions and recommendations.
When the system is accurately implemented and followed, the certification of the OH&SMS by an external body is a breeze, a formality (step 7).
An example of a 24-step certification project plan is presented in annex 01. 
An appropriate method for evaluating the performance of your OH&Soccupational health and safety management system is the RADAR logic model of excellence EFQM (European Foundation for Quality Management) with its nine criteria and overall score of 1000 points.
The Deming cycle (figure 1-3) is applied to control of any processactivities which transform inputs into outputs (see also ISO 9000, 3.4.1) that impacts on occupational health and safety (OH&Soccupational health and safety). The PDCA cycles (Plan, Do, Check, Act) are a universal base for continual improvement.
- Plan – prepare, demonstrate leadership and worker participation, define context, issues and processes, establish OH&S policy and objectives, identify hazards, assess risks (ISO 45001, clauses 4, 5 and 6)
- Do – develop, demonstrate leadership and worker participation, implement processes, training, communication, awareness and documented information (ISO 45001, clauses 5, 7 and 8)
- Check – understand, demonstrate leadership and worker participation, inspect (monitor and measure), verify, evaluate, conduct audits and management review (ISO 45001, clauses 5 and 9)
- Act – adapt, improve, demonstrate leadership and worker participation, decide, treat nonconformities, react with corrective actions and find new improvements (new PDCA cycle), (ISO 45001, clauses 5 and 10)
For more information on the Deming cycle and his 14 points of management theory you can consult the classic book "Out of the crisis", W. Edwards Deming, MIT press, 1982.

.jpg)