4 Cost categories .gif)
The costs of obtaining quality (COQcosts of obtaining quality) fall into two main groups:
- compliance costs (CC) and
- non-compliance costs (NCC)
Compliance costs (CC), also called unavoidable costs or quality costs, are the costs of doing it right the first time, every time. These are investments.
Non-compliance costs (NCC), also called avoidable costs or non-quality costs, are the costs associated with anything that was not done right the first time. These are losses.
As shown in figure 4-1, compliance costs (CC) fall into two categories:
- prevention costs (P) and
- detection costs (D)
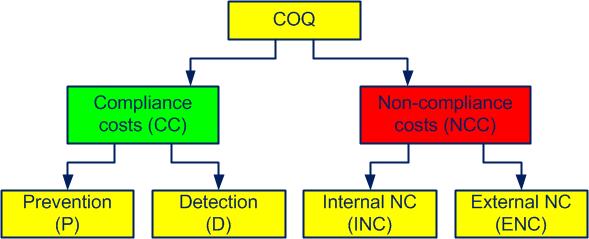
Figure 4-1. Cost categories
Non-compliance costs (NCC) fall into the following categories:
- costs of internal non-conformities (INC) and
- costs of external non-conformities (ENC)
4.1 Prevention
Prevention costs, examples

Prevention costs (P) are the expenses incurred to avoid nonconformities (NC). This category mainly includes the following types:
- quality function (salaries, documentation, preventive actions, management reviews, miscellaneous expenses)
- supplier evaluation (selection, supplier audits)
- staff awareness (motivation)
- staff training
- preventive maintenance
- internal system audits
- design of new products, processes
- improvement of processes, products, equipment (Kaizen activities)
- evaluation of personnel upon hiring
- contract review
- environment function (salaries, facilities, miscellaneous costs)
- occupational health and safety function (salaries, equipment, signage)
- FMEA
- PPAP
- value analysis
- SPC
The quality manager notes that the administrative processing department is experiencing significant delays due to a high absenteeism rate.
Proposed preventive actions:
• internal investigation to understand the root causes (atmosphere, workload)
• improvement of working conditions (flexible hours, ergonomics)
• role enhancement and recognition plan
• recruitment of temporary reinforcements
Expected results:
• decrease in absenteeism
• improvement of productivity and service quality
4.2 Detection
Detection costs examples

Detection costs (D, also called appraisal, inspection, evaluation, measurement) are the expenses incurred to verify the existence of nonconformities (NC). This category mainly includes the following types:
- inspection and test function (salaries, documentation, inspections on receipt, in production, on shipment)
- validations (new projects, processes, equipment, miscellaneous costs)
- verifications (tests including destructive, laboratory costs, inventories, evaluation of products in stock)
- purchase or construction of measuring and monitoring equipment
- monitoring and measurement (samples and specimen)
- depreciation of equipment
- metrology (calibration and checks of measuring and monitoring equipment)
- annual staff interviews
- internal process and product audits
- external audits (certification)
- customer satisfaction surveys
The quality manager analyzes the COQ table and realizes that production waste mainly comes from rework costs and scrap.
Proposed detection actions:
• understand root causes (5 Ws, Pareto chart, Ishikawa diagram)
• improve the work environment (5 S)
• improve operator training
• regularly audit non-conformity trends (histogram, check card)
• strengthen preventive maintenance of tools and equipment
Expected results:
• upstream detection of root causes
• reduced scrap
4.3 Internal NC
Internal NC examples

The costs of internal nonconformities (INC, also called anomalies, failures, defects, malfunctions and scrap) are the expenses incurred because of nonconformities (NC) that the customeranyone who receives a product (see also ISO 9000, 3.3.5) does not perceive. This category mainly includes the following types:
- processing of nonconformities (analysis, recording, sorting)
- curative actions (touch-ups, repairs, re-conditioning, re-tests, additional 100% inspection before being put back into the normal flow)
- scrap (including handling, storage, transport, destruction, disposal)
- abnormal consumption of raw materials, energy, information
- finished or in-process products downgraded
- losses due to unusable purchases (supply errors, changes to the finished product)
- losses due to finished products in stock (logistical errors)
- accidental pollution (depollution installations, discharge inspections, fines, compensation)
- workplace accidents (sick leave, replacement staff)
- staff rotation (training new employees)
- absenteeism (unpredictable, replacement staff)
- curative maintenance (equipment and machinery out of order, production stoppages)
- corrective actions (unplanned changes to product, process, tooling, tools, equipment and documentation)
- additional tests
- finance costs (accounting errors, delayed invoicing)
An example of defect codes (solder and PCB) is shown in annex 04. 
The quality manager is informed that the rate of defective printed cards leaving the line has reached 5%, resulting in high rework and warranty costs. Work instructions are not standardized.
Proposed actions to reduce internal nonconformities:
• invest in automated visual inspections (camera and AI)
• enhanced operator training on the different types of defects
• preventive equipment maintenance
Expected results:
• reduction of defective cards under 1%
• fast and effective ROI (return on investment)
4.4 External NC
External NC examples

The costs of external nonconformities (ENC) are the expenses incurred because of nonconformities (NC) that the customer receives. This category mainly includes the following types:
- disputes with customers (lawsuits, complaints, compensation)
- exceptional transport (helicopter, plane, taxi, express parcel)
- customer complaints and returns, products under warranty, withdrawals (penalties, return reimbursement, transport, analysis time and action plan)
- supplier complaints
- out-of-warranty after-sales service (part of the costs graciously offered to the customer)
- reductions granted (discounts, rebates)
- late penalties (fees for failure to meet deadlines)
- reimbursement of damage caused to others
- legal fees
- insurance premium
- expert fees
- subcontracting fees imposed (recall, withdrawal, return, destruction, disposal)
The quality manager understands that the company is experiencing 10% late deliveries, resulting in penalties and lost contracts.
Proposed actions to reduce delays:
• internal survey to understand root causes (poorly planned routes, frequent vehicle breakdowns)
• GPS vehicle tracking
• improved preventive vehicle maintenance
• driver training in eco-driving
Expected results:
• 50% reduction in delays
• 30% reduction in breakdowns
• fast and effective ROI
The rest of the T 57 COQ approach training is accessible on this page.
