ISO 14971 requirements - Application of risk management to medical devices - version 2019
07/01/2024
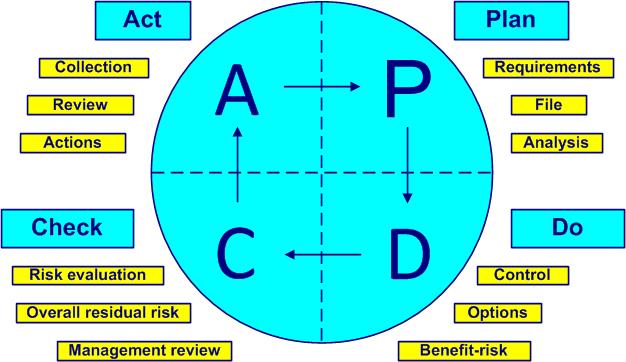
Quiz requirements ISO 14971 version 2019 You want to familiarize yourself with the structure of the standard, identify and understand the requirements of ISO 14971 version 2019, then it's up to you to play!
|
Nb
|
Clause
|
cycle PDCA
|
Requirements Nb
|
Amount
|
|
4
|
General requirements | Plan |
1 ÷ 40
|
40
|
| 5 | Risk analysis | Plan |
41 ÷ 64
|
24 |
| 6 | Risk evaluation | Check |
65 ÷ 70
|
6
|
| 7 | Risk control | Do |
71 ÷ 98
|
28 |
| 8 | Evaluation of overall residual risk | Check |
99 ÷ 103
|
5 |
| 9 | Risk management review | Check | 104 ÷ 111 | 8 |
| 10 | Production and post-production activities | Act | 112 ÷ 134 | 23 |
|
Total
|
134 |
|||
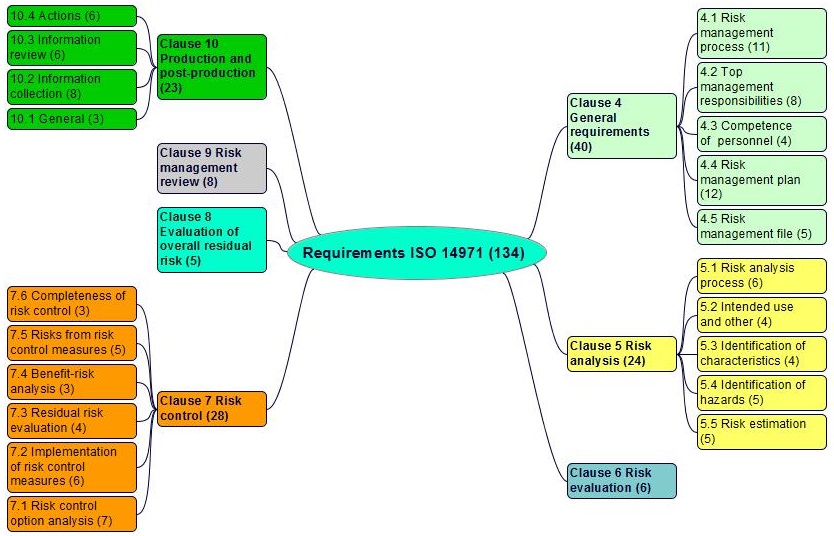
ISO 14971 requirements in clauses 4 to 10
Notice 1. Any requirement normally begins with "The manufacturer shall...". To simplify we present the requirements directly starting with the verb.
Notice 2. Sub-clauses of the standard are replaced by the paragraph sign §, for simplification.
|
ISO 14971 - Requirements and comments
|
||||
|
Nb
|
Clause sub-clause
|
Requirement
|
PDCA cycle, links, comments
|
|
|
General requirements
|
||||
|
4.1
|
Risk management process
|
|||
|
1
|
4.1 a)
|
Establish, implement, document and maintain a process |
For identifying hazards and hazardous situations of the MD | |
|
2
|
4.1 b)
|
Establish, implement, document and maintain a process |
For estimating and evaluating the associated risks | |
|
3
|
4.1 c)
|
Establish, implement, document and maintain a process |
For controlling these risks | |
|
4
|
4.1 d)
|
Establish, implement, document and maintain a process |
For monitoring the effectiveness of the risk control measures | |
|
5
|
4.1
|
Apply this process throughout the life cycle |
Of the MD | |
|
6
|
4.1
|
Include the following elements |
Such as risk analysis, cf. ISO 13485, clause 7 | |
|
7
|
4.1
|
Include the following elements |
Such as risk evaluation, cf. ISO 13485, clause 7 | |
|
8
|
4.1
|
Include the following elements |
Such as risk control, cf. ISO 13485, clause 7 | |
|
9
|
4.1
|
Include the following elements |
Such as production and post-production, cf. ISO 13485, clause 7 | |
|
10
|
4.1
|
Incorporate the appropriate parts of the risk management process |
When a documented product realization process exists | |
|
11
|
4.1
|
Check compliance of risk management process |
By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file), cf. annex B.2 | |
|
4.2
|
Top management responsibilities
|
|
||
|
12
|
4.2
|
Provide evidence of top management commitment to the manage risk process | By ensuring the provision of available adequate resources | |
| 13 | 4.2 | Provide evidence of top management commitment to the manage risk process | By ensuring the assignment of competent personnel for risk management, cf. § 4.3 and annex A.2.4.3 | |
| 14 | 4.2 | Define and document a policy (regarding top management) | For establishing criteria for risk acceptability, cf. ISO/TR 24971 | |
| 15 | 4.2 | Provide a framework (related to the policy) | Ensuring that criteria are based on national or regional regulations and relevant international standards | |
| 16 | 4.2 | Take into account available information (related to the policy) |
Such as the generally acknowledged state of the art and known stakeholder concerns |
|
| 17 | 4.2 | Review the suitability of the risk management process at planned intervals (regarding top management) |
To ensure continuing effectiveness of the risk management process. This review can be part of the audit of the quality management system |
|
| 18 | 4.2 | Document any decisions (regarding top management) | And action taken | |
| 19 | 4.2 | Check compliance of policy | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
4.3
|
Competence of personnel
|
|||
|
20
|
4.3
|
Recruit competent personnel |
In order to master MD risk management activities, based on the required knowledge and experience. Know how to implement the risk management process |
|
| 21 | 4.3 | Develop the necessary knowledge and experience | In order to be able to use specific MDs, technologies or techniques. Know how the MD is built, works, is manufactured and is actually used. | |
| 22 | 4.3 | Maintain appropriate records (objective evidence) | On the competence of personnel. These records are confidential and do not enter into the risk management file | |
| 23 | 4.3 | Check compliance of competence | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
4.4
|
Risk management plan
|
|
||
| 24 | 4.4 | Plan risk management activities | The plan ensures that no essential elements are forgotten. Monitor plan compliance with the risk management process | |
| 25 | 4.4 | Establish a risk management plan | For every MD, cf. ISO/TR 24971 | |
| 26 | 4.4 | Document a risk management plan | For every MD | |
| 27 | 4.4 | Include the risk management plan in the risk management file | Cf. § 4.5 | |
| 28 | 4.4 a) | Include in the risk management plan | The scope of activities, the description of the MD, the phases of the life cycle for which each element of the plan is applicable | |
| 29 | 4.4 b) | Include in the risk management plan | Responsibilities and authorities. Allows you not to forget any responsibilities | |
| 30 | 4.4 c) | Include in the risk management plan | Requirements for reviewing risk management activities. In principle, it is the responsibility of top management | |
| 31 | 4.4 d) | Include in the risk management plan | Risk acceptability criteria; the manufacturer determines the acceptable risks. Criteria to set before analyzing the risks | |
| 32 | 4.4 e) | Include in the risk management plan | The method for evaluating the overall residual risk and the criteria for acceptability of this risk, cf. clause 8 | |
| 33 | 4.4 f) | Include in the risk management plan | Verification of the implementation and effectiveness of risk control measures, so as not to forget any element, cf. § 7.2 | |
| 34 | 4.4 g) | Include in the risk management plan | Collecting and reviewing relevant production and post-production information, cf. ISO/TR 24971 | |
| 35 | 4.4 | Make a record of the changes of the plan | In order to update the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
|
Risk management file
|
||||
| 36 | 4.5 | Establish and maintain a risk management file |
For each MD, guarantee the completion of the risk management process in its entirety. The recommendations of ISO/TR 24971 for establishing the risk management file are relevant |
|
| 37 | 4.5 | Provide traceability for each identified hazard | In relation to the risk analysis | |
| 38 | 4.5 | Provide traceability for each identified hazard | In relation to the risk evaluation | |
| 39 | 4.5 | Provide traceability for each identified hazard | In relation to the implementation and verification of the risk control measures | |
| 40 | 4.5 | Provide traceability for each identified hazard | In relation to the results of evaluation of the residual risks | |
|
5
|
Risk analysis
|
|||
|
5.1
|
Risk analysis process
|
|
||
| 41 | 5.1 | Perform a risk analysis process |
For every MD, cf. §§ 5.2 to 5.5 and ISO/TR 24971. Use any information from a similar MD in order to save time |
|
| 42 | 5.1 | Make records of the activities and results of the risk analysis process | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 43 | 5.1 a) | Include in the documentation the identification and description of every MD | For every analyzed MD | |
| 44 | 5.1 b) | Include in the documentation the person and organization who carried out the risk analysis | For every MD, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 45 | 5.1 c) | Include in the documentation the scope and date of the risk analysis | For every MD, cf. § 4.5, proof that the analysis has been completely carried out | |
| 46 | 5.1 | Check compliance of risk analysis | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
5.2
|
Intended use and reasonably foreseeable misuse
|
|
||
| 47 | 5.2 | Document the intended use | For each MD. Take into account use by a professional or not, the intended medical indication, the target population, the part of the body or the type of tissue interacting, the user profile, the context of use, the operating principle | |
| 48 | 5.2 | Document also reasonably foreseeable misuse | For each MD, situations other than those provided by the manufacturer, identify the hazards of the potential misuse of the MD, cf. ISO/TR 24971 | |
| 49 | 5.2 | Maintain the MD documentation | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 and IEC 62366-1, § 3.23 | |
| 50 | 5.2 | Check compliance of use | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
5.3
|
Identification of characteristics related to safety
|
|
||
| 51 | 5.3 | Identify and document qualitative and quantitative characteristics of every MD | That may affect the safety of the medical device, including the operating principle of the MD, its intended use and reasonably foreseeable misuse, cf. ISO/TR 24971 | |
| 52 | 5.3 | Define limits of those characteristics | That may affect the safety of the MD, cf. IEC 62366-1 | |
| 53 | 5.3 | Maintain the MD documentation | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 54 | 5.3 | Check compliance of characteristics | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
5.4
|
Identification of hazards and hazardous situations
|
|
||
| 55 | 5.4 | Identify and document known and foreseeable for every MD | In relation to intended use, reasonably foreseeable misuse and safety features under normal and abnormal conditions, cf. §§ 5.2 and 5.3 | |
| 56 | 5.4 |
Take into consideration, for each identified hazard, the reasonably foreseeable sequences or combinations of events |
That can result in a hazardous situation | |
| 57 | 5.4 | Identify and document hazardous situations and potential harm | That can result, cf. annex C and ISO/TR 24971 | |
| 58 | 5.4 | Maintain the MD documentation | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 59 | 5.4 | Check compliance of hazards and hazardous situations | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
Risk estimation
|
||||
| 60 | 5.5 | Estimate, for each hazardous situation and every MD the associated risks |
Using the available information, cf. ISO/TR 24971. Examples: standards, scientific studies, field data, usability testing, clinical evidence, simulations, expert opinions |
|
| 61 | 5.5 |
Establish a list of all possible consequences for hazardous situations whose probability of occurrence of harm cannot be estimated |
In order to evaluate and control (decrease) risks | |
| 62 | 5.5 | Make a record of these activities | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 63 | 5.5 | Make a record of the system used for categorization of probability of occurrence of harm and severity of harm | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 64 | 5.5 | Check compliance of risk estimation | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
6
|
Risk evaluation
|
Comparer (Check)
|
||
| 65 | 6 | Evaluate the estimated risks | For every hazardous situation identified | |
| 66 | 6 | Determine if the risk is acceptable or not | For each hazardous situation identified, based on the risk acceptability criteria of the risk management plan, cf. § 4.4 | |
| 67 | 6 | Treat the risk as residual risk | When the risk is acceptable. Do not apply the requirements given in §§ 7.1 to 7.5. Apply requirements given in § 7.6 | |
| 68 | 6 | Perform risk control activities | When the risk is not acceptable. Apply requirements given in §§ 7.1 to 7.5 | |
| 69 | 6 | Make a record of the results of risk evaluation | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 70 | 6 | Check compliance of risk evaluation | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
7
|
Risk control
|
|||
|
7.1
|
Risk control option analysis
|
|||
|
71
|
7.1
|
Determine risk control measures | In order to reduce the risks to an acceptable level, cf. annex A.2.7.1 and guide ISO/IEC 63 | |
|
72
|
7.1 a)
|
Use risk control options such as inherently safe design and manufacture | In order of priority a, b, c. Apply relevant standards for risk control options. Examples: eliminating hazardous substances, using separate production lines, adding visual controls | |
|
73
|
7.1 b)
|
Use risk control options such as protective measures in the MD itself or in the manufacturing process |
In order of priority a, b, c. Apply relevant standards for risk control options | |
|
74
|
7.1 c)
|
Use risk control options such as information for safety or training of users | In order of priority a, b, c. Apply relevant standards for risk control options, cf. ISO/TR 24971 annex E | |
|
75
|
7.1
|
Make a record of risk control measures selected | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
|
76
|
7.1
|
Conduct a benefit-risk analysis of the residual risk | When risk reduction is not practicable, proceed to § 7.4 | |
|
77
|
7.1
|
Check compliance of risk control option analysis | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
7.2
|
Implementation of risk control measures
|
|
||
| 78 | 7.2 | Implement the risk control measures | Compared to the chosen option, cf. § 7.1 | |
| 79 | 7.2 | Verify the implementation of each risk control measure | Compared to the chosen option, cf. § 7.1, l'ISO 13485 and ISO/TR 24971 | |
| 80 | 7.2 | Make a record of every verification done | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 81 | 7.2 | Verify the effectiveness of the risk control measures | As part of the verification and validation of design and development, cf. annex A.2.7.2, ISO 14155 and ISO 20916 | |
| 82 | 7.2 | Make a record of the results of the verification | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 83 | 7.2 | Check compliance of risk control measures | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
7.3
|
Residual risk evaluation
|
|
||
|
84
|
7.3
|
Evaluate the residual risk, after the implementation of risk control measures | Using risk acceptability criteria defined in the risk management plan, cf. 4.4 | |
|
85
|
7.3
|
Make a record of the evaluation | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
|
86
|
7.3
|
Consider further risk control measures | When the residual risk is judged not, go back to § 7.1 | |
| 87 | 7.3 | Check compliance of residual risk evaluation | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
7.4
|
Benefit-risk analysis
|
|||
| 88 | 7.4 | Proceed to § 7.5 |
When the benefits are greater than the residual risk. When the residual risk is not considered acceptable, it can be determined whether the benefits outweigh the residual risk. We can modify the MD and its intended use; return to § 5.2), cf. ISO/TR 24971 and the experimental standard XP S99-223 |
|
| 89 | 7.4 | Make a record of the results of the benefit-risk analysis | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 90 | 7.4 | Check compliance of benefit-risk analysis | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
7.5
|
Risks arising from risk control measures
|
|||
| 91 | 7.5 | Review the effects of the risk control measures |
Considering whether new hazards or hazardous situations are present |
|
| 92 | 7.5 | Review the effects of the risk control measures |
By considering whether the new risk control measures have an impact on the risks of hazardous situations already identified |
|
| 93 | 7.5 | Manage any new or increased risk | ||
| 94 | 7.5 | Make a record of the results of the risk review |
In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 |
|
| 95 | 7.5 | Check compliance of new risks |
By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) |
|
|
Completeness of risk control
|
||||
| 96 | 7.6 | Review the risk control activities | In order to ensure that the risks of all identified hazardous situations have been addressed and that risk control activities are completed | |
| 97 | 7.6 | Make a record of the review | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 98 | 7.6 | Check compliance of completeness of risk control | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
8
|
Evaluation of overall residual risk
|
Check | ||
| 99 | 8 | Evaluate the overall residual risk posed by the MD, after all risk control measures have been implemented and verified | Considering the contributions of all residual risks, relative to the benefits for the intended use, according to the risk management plan, cf. § 4.4 e and ISO/TR 24971 | |
| 100 | 8 | Inform users of significant residual risks | When the overall residual risk is judged as acceptable, cf. annex A.2.8 | |
| 101 | 8 | Include the necessary information in the accompanying documentation |
In order to list the residual risks. When the overall residual risk is not considered as acceptable, we can consider implementing other risk control measures (return to § 7.1) or modify the MD or its use (return to § 5.2) |
|
| 102 | 8 | Make a record of the results of the evaluation of the overall residual risk | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 103 | 8 | Check compliance of evaluation of overall residual risk | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) and accompanying documentation | |
|
9
|
Risk management review
|
|||
| 104 | 9.1 | Review the execution of the risk management plan | Prior to release for commercial distribution of the MD | |
| 105 | 9.1 | Ensure the review at least | That the risk management plan has been implemented appropriately | |
| 106 | 9.1 | Ensure the review at least | That the overall residual risk is acceptable | |
| 107 | 9.1 | Ensure the review at least | That appropriate methods for collecting and reviewing production and post-production information are in place | |
| 108 | 9.1 | Make a record of the results of the review | And maintain it in the form of a risk management report | |
| 109 | 9.1 | Include the results of this review | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 110 | 9.1 | Assign the responsibility for review to persons having the appropriate authority | Cf. §§ 4.4 b) and 4.5 | |
| 111 | 9.1 | Check compliance of risk management review | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
10
|
Production and post-production activities
|
|||
|
10.1
|
General
|
|||
| 112 | 10.1 | Establish, document and maintain a system to actively collect and review information relevant to the MD | During design, production and post-production, cf. ISO 13485, §§ 7.3.3, 8.2.1, 8.4, 8.5 and ISO/TR 24971 | |
| 113 | 10.1 | Consider appropriate methods for the collection and processing of information | When establishing the MD information collection and review system | |
| 114 | 10.1 | Check compliance of appropriate documents | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file). See also ISO/TR 20416 | |
|
Information collection
|
|
|||
| 115 | 10.2 a) | Collect information generated during production | And monitoring the production process. The information collection and post-market surveillance plan are described in the technical report ISO/TR 20416 | |
| 116 | 10.2 b) | Collect information generated by the user | Because no simulation can replace the MD in the hands of the end user, cf. ISO 14155 | |
| 117 | 10.2 c) | Collect information generated by those accountable for the installation and use of the MD | And maintenance of the MD | |
| 118 | 10.2 d) | Collect information generated by the supply chain | Such as suppliers of components or subsystems and software | |
| 119 | 10.2 e) | Collect publicly available information | Coming from many sources, including similar MDs | |
| 120 | 10.2 f) | Collect information related to the state of art | Generally acknowledged, cf. ISO/TR 24971 | |
| 121 | 10.2 | Consider the information about similar MD | And other similar products on the market | |
| 122 | 10.2 | Check compliance of information collection | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
10.3
|
Information review
|
|||
| 123 | 10.3 | Review the information collected for possible relevance to safety | In order to determine whether new hazards or hazardous situations have emerged | |
| 124 | 10.3 | Review the information collected for possible relevance to safety | In order to determine whether a risk of a hazardous situation is no longer acceptable | |
| 125 | 10.3 | Review the information collected for possible relevance to safety | In order to determine whether the overall residual risk is no longer acceptable, cf. § 7.4 | |
| 126 | 10.3 | Review the information collected for possible relevance to safety | In order to determine whether the generally accepted state of the art has evolved | |
| 127 | 10.3 | Make a record of the results of the review | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 128 | 10.3 | Check compliance of information review | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file). Use statistical methods, if necessary, cf. ISO 10017 | |
| 10.4 |
Actions
|
|
||
| 129 | 10.4 | Review the risk management file, when the collected information is determined to be relevant to safety | And determine whether a re-evaluation of old or new risks is necessary. Take into account developments in the state of the art, new MDs, changes in risk perception | |
| 130 | 10.4 | Evaluate the impact on risk control measures, when the residual risk is no longer acceptable | The impact should be considered as an input for modification of the MD. It is necessary to examine the need for actions of MDs on the market | |
| 131 | 10.4 | Make a record of all decisions and actions | In the risk management file, cf. § 4.5 | |
| 132 | 10.4 | Evaluate the impact on risk management activities | Previously implemented | |
| 133 | 10.4 | Consider the results of this evaluation as an input | For review of the adequacy of the risk management process by top management | |
| 134 | 10.4 | Check compliance of actions | By inspection of appropriate documents (risk management file) | |
|
|
|
|
||