ISO 42001 requirements artificial intelligence management system version 2023
16/01/2026
Quiz requirements ISO 42001 version 2023 You want to familiarize yourself with the structure of the standard, identify and understand the requirements of ISO 42001 version 2023, then it's up to you to play!
The quiz "ISO 42001 Requirements version 2023" will help you understand the main requirements of the standard.
The questions (requirements) for this quiz are 85, don't panic. The requirements of the standard are 206 but these 85 requirements are among the most important, so don't hesitate to learn in a fun way!
Don't think that you can complete this quiz in less than an hour, or even two hours, unless of course you are a little genius!
The 206 requirements (shall) of clauses 4 to 10 and annex A of ISO 42001 are broken down as follows:
|
No
|
Clause
|
PDCA cycle
|
Requirement No
|
Quantity
|
|
4
|
Context | Plan |
1 to 13
|
13
|
| 5 | Leadership | Plan, Do, Check, Act |
14 to 32
|
19 |
| 6 | Planning | Plan |
33 to 90
|
58
|
| 7 | Support | Do |
91 to 114
|
24 |
| 8 | Operation | Do |
115 to 131
|
17 |
| 9 | Performance | Check | 132 to 156 | 25 |
| 10 | Improvement | Act | 157 to 168 | 12 |
| Annex A.2 | Check | 169 to 171 | 3 | |
| Annex A.3 | Check | 172 to 173 | 2 | |
| Annex A.4 | Check | 174 to 178 | 5 | |
| Annex A.5 | Check | 179 to 182 | 4 | |
| Annex A.6 | Check | 183 to 191 | 9 | |
| Annex A.7 | Check | 192 to 196 | 5 | |
| Annex A.8 | Check | 197 to 200 | 4 | |
| Annex A.9 | Check | 201 to 203 | 3 | |
| Annex A.10 | Check | 204 to 206 | 3 | |
|
Total
|
206
|
|||
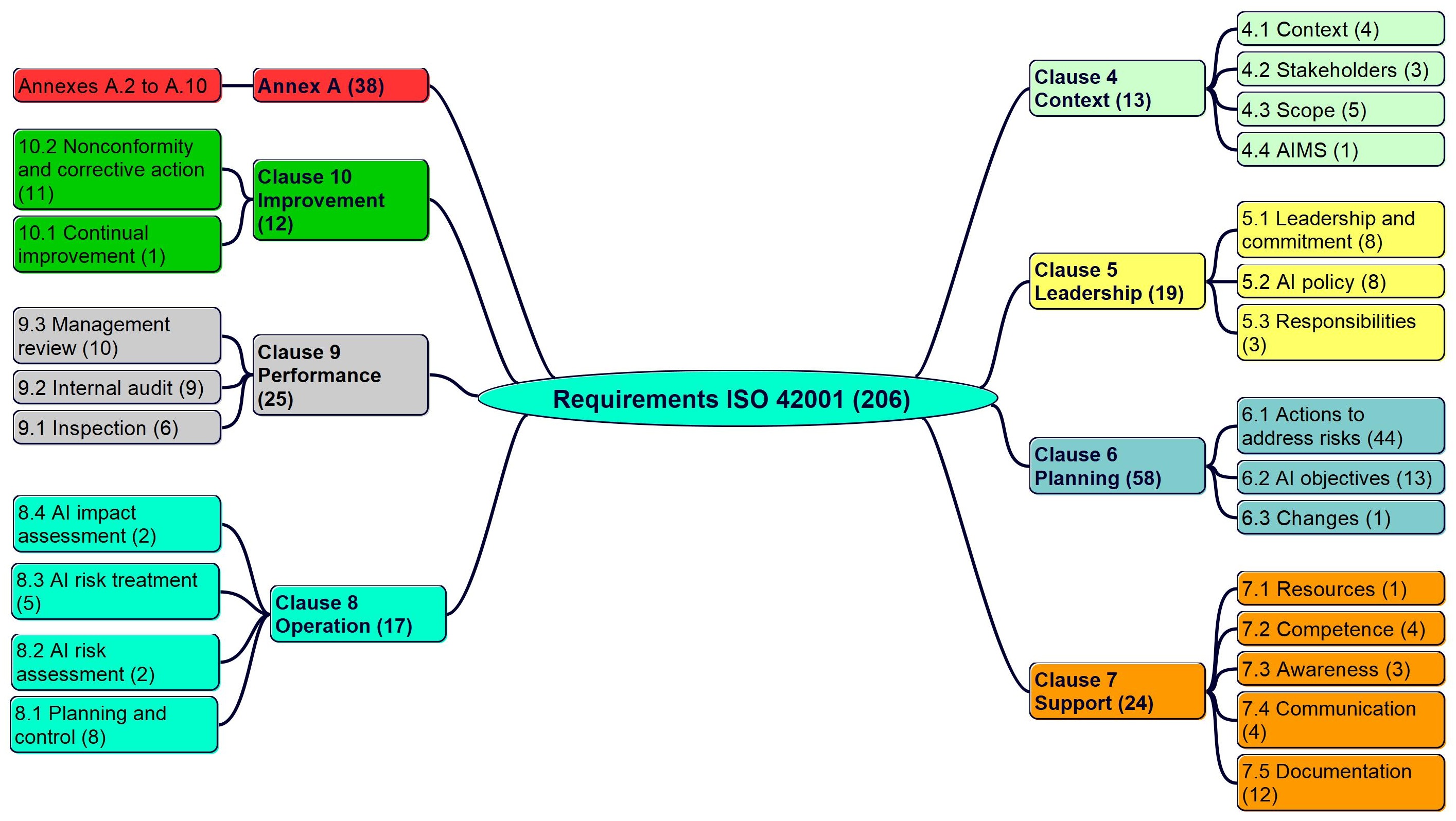
Requirements in ISO 42001 clauses, sub-clauses and annex A
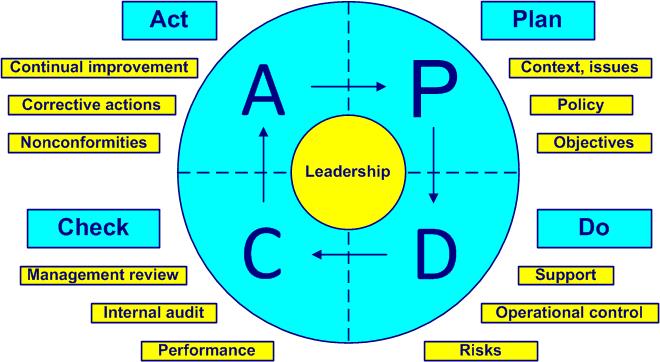
Deming PDCA cycle
Note. Any requirement normally begins with "The organization shall ...". For simplicity we present the requirements directly starting with the verb.
|
ISO 42001 - Requirements and comments version 2023
|
||||
|
No
|
Clause
(sub-clause)
|
Requirement
|
PDCA cycle, links, comments
|
|
|
Context
|
||||
|
4.1
|
The organization and its context
|
|||
|
1
|
4.1
|
Determine external and internal issues | Understand everything that can influence the purpose (mission) of the company (corporate culture, innovation, strategic orientation, competition, market, obligations, working time, working conditions) and its ability to obtain the expected results of the AIMS. See sub-clauses 6.1 and 7.5.1 | |
|
2
|
4.1
|
Determine whether climate change is a relevant issue |
Changes regarding climate-related actions, see Amendment 1 to ISO 14001: 2020 |
|
|
3
|
4.1
|
Consider the intended purpose of the AI system | That are developed, provided or used by the organization | |
|
4.2
|
Stakeholders
|
|
||
|
5
|
4.2
|
Determine stakeholders | Concerned with the AIMS, such as laws, contracts and others. See sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
| 6 | 4.2 | Determine needs and expectations of stakeholders | Needs and expectations related to requirements and obligations. Stakeholders may have requirements related to climate change. | |
| 7 | 4.2 | Determine requirements concerned by the AIMS | Requirements addressed by the AIMS | |
|
4.3
|
Scope
|
|||
|
8
|
4.3
|
Determine the scope of the AIMS | (Administrative) limits and applicability | |
| 9 | 4.3 | Take into account external and internal issues | "To determine hazards is to reduce risks". Cf. sub-clause 4.1 | |
| 10 | 4.3 | Take into account the requirements of the stakeholders | When changing processes, requirements, infrastructure. See sub-clause 4.2 | |
| 11 | 4.3 | Make the scope available | As a document | |
| 12 | 4.3 | Determine the organization's activities in relation to the requirements of ISO 42001 | Related to leadership, planning, support, operation, performance, evaluation, improvement, measurement and objectives | |
|
4.4
|
Artificial intelligence management system
|
|
||
| 13 | 4.4 | Establish, implement and maintain and improve the AIMS |
"If you cannot describe what you are doing as a process, you do not know what you're doing". Edwards Deming. Including the necessary processes and their interactions. Required processes:
|
|
|
5
|
Leadership
|
|||
|
5.1
|
Leadership and commitment
|
|||
| 14 | 5.1 | Ensure that the AI policy and objectives are established |
"When you sweep the stairs, you start at the top. Romanian proverb." Ensure compatibility with strategic direction. Top management is showing leadership. Affirm top management's commitment to the AIMS |
|
| 15 | 5.1 | Ensure that AIMS requirements are integrated into business processes | Show leadership | |
| 16 | 5.1 | Ensure that the necessary resources for the AIMS are available | Resources to establish, apply, maintain and improve the AIMS. Cf. sub-clause 4.4 | |
| 17 | 5.1 | Communicate on the importance of an effective AIMS | And comply with the requirements of ISO 42001 | |
| 18 | 5.1 | Ensure that the AIMS achieves the intended results | Commitment, responsiveness and active support from top management | |
| 19 | 5.1 |
Guide and support people |
In order to contribute to the performance of the AIMS | |
| 20 | 5.1 | Promote continual improvement | "Employees first, customers second. Vineet Nayar." Show leadership. Cf. clause 10 | |
| 21 | 5.1 | Help those affected to show leadership | When necessary for their area of responsibility | |
|
5.2
|
AI policy
|
|
||
| 22 | 5.2 a | Establish an AI policy | Taking into account the mission of the organization. Keep the policy up to date. Cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
| 23 | 5.2 b | Provide a framework for establishing AI objectives | Cf. sub-clause 6.2 and Annex A.2. A guide to implementing the controls is available in Annex B.2 of ISO 42001 | |
| 24 | 5.2 c | Commit to meet applicable requirements | Regarding the AIMS | |
| 25 | 5.2 d | Commit to continual improvement of the AIMS | Cf. clause 10 | |
| 26 | 5.2 | Make the AI policy available | As a document. Cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
| 27 | 5.2 | Refer as relevant | To other organizational policies | |
| 28 | 5.2 | Communicate the AI policy | Within the organization | |
| 29 | 5.2 | Keep the AI policy available to stakeholders | As appropriate | |
|
5.3
|
Roles, responsibilities and authorities
|
|
||
| 30 | 5.3 | Ensure that responsibilities and authorities for the AIMS are assigned | And communicated at all levels of the organization. "Responsibility cannot be shared. Robert Heinlein". Cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
| 31 | 5.3 a | Ensure that the AIMS meets the requirements of the ISO 42001 standard | And who has the responsibility and authority at all levels of the organization. Remember that in the end top management is fully responsible (cf. sub-clause 5.1) | |
| 32 | 5.3 b | Submit reports on AIMS performance to top management on a regular basis | By assigning responsibility and authority by name, cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
|
6
|
Planning
|
|||
|
6.1
|
Actions to address risks
|
|||
|
6.1.1
|
General
|
|
||
| 33 | 6.1.1 | Determine the risks and opportunities | Risk management is based on the ISO 31000 standard (see training course T 61). Cf. sub-clause 4.1 for issues and sub-clause 4.2 for requirements. An inventory of the situation is always useful before planning. "Any decision involves a risk. Peter Barge" | |
| 34 | 6.1.1 | Ensure that the AIMS can achieve its intended results | In order to anticipate or reduce side effects | |
| 35 | 6.1.1 | Prevent or reduce undesired effects |
Cf. sub-clause 6.1.3 |
|
| 36 | 6.1.1 | Achieve continual improvement | Continual improvement approach, cf. clause 10 | |
| 37 | 6.1.1 | Establish and maintain AI risk criteria | For all processes of the AIMS | |
| 38 | 6.1.1 | Distinguishing between acceptable and unacceptable risks | Cf. sub-clause 6.1.2 | |
| 39 | 6.1.1 | Perform AI risk assessments | Cf. sub-clause 6.1.2 | |
| 40 | 6.1.1 | Conduct AI risk treatment | Cf. sub-clause 6.1.2 | |
| 41 | 6.1.1 | Assess AI risk impacts | Cf. sub-clause 6.1.2 | |
| 42 | 6.1.1 | Determine the risks and opportunities | Cf. sub-clause 6.1.2 | |
| 43 | 6.1.1 | Determine the risks and opportunities | According to the domain and application of an AI system | |
| 44 | 6.1.1 | Determine the risks and opportunities | According to the intended use | |
| 45 | 6.1.1 | Distinguishing between acceptable and unacceptable risks | According to the context described in 4.1 | |
| 46 | 6.1.1 | Plan how to integrate and implement the actions | Into its AI management system processes | |
| 47 | 6.1.1 | Plan how to evaluate the effectiveness | Of these actions | |
| 48 | 6.1.1 | Retain records on actions taken | In order to identify and address AI risks and opportunities, cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
|
6.1.2
|
Risk assessment
|
|||
| 49 | 6.1.2 a | Apply an AI risk assessment process | That is informed by and aligned with the AI policy and objectives | |
| 50 | 6.1.2 b | Apply an AI risk assessment process | That is designed such that repeated AI risk assessments can produce consistent, valid and comparable results. Impossible physical and intellectual challenge. Cf. the Oxebridge blog :"iso-risk-management-can-now-be-infallible" | |
| 51 | 6.1.2 c | Identify risks | That aid or prevent achieving its AI objectives | |
| 52 | 6.1.2 d 1 | Analyze AI risks | To assess the potential consequences if the risks were to materialize | |
| 53 | 6.1.2 d 2 | Assess the realistic likelihood of the identified risks | Where applicable | |
| 54 | 6.1.2 d 3 | Determine the levels of risks |
Following the AI risk analysis |
|
| 55 | 6.1.2 e 1 | Evaluate the AI risks | To compare the results of the risk analysis with the risk criteria, cf. sub-clause 6.1.1 | |
| 56 | 6.1.2 e 2 | Prioritize the risks | Assessed for risk treatment | |
| 57 | 6.1.2 | Retain records about the AI risk assessment process | Cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
|
6.1.3
|
Risk treatment
|
|||
| 58 | 6.1.3 a | Define and apply an AI risk treatment process | In order to select the risk treatment options taking into account the results in 6.1.2 | |
| 59 | 6.1.3 b | Determine all controls that are necessary to implement | The AI risk treatment options chosen | |
| 60 | 6.1.3 b | Compare the controls with those in Annex A | In order to verify that no necessary controls have been omitted | |
| 61 | 6.1.3 c | Consider the controls from Annex A that are relevant | For the implementation of the AI risk treatment options | |
| 62 | 6.1.3 d | Identify if additional controls are necessary beyond those in Annex A | In order to implement all risk treatment options | |
| 63 | 6.1.3 e | Consider the guidance in Annex B | In order to implement the controls determined in b) and c) | |
| 64 | 6.1.3 f | Produce a statement of applicability | That contains the necessary controls determined in b), c) and d) | |
| 65 | 6.1.3 g | Formulate an AI risk treatment plan | In order to implement the controls determined in b) and c) | |
| 66 | 6.1.3 | Obtain approval from the designated management for the AI risk treatment plan | And for acceptance of residual AI risks | |
| 67 | 6.1.3 | Align the necessary controls to the objectives | Cf. sub-clause 6.2 | |
| 68 | 6.1.3 | Make the necessary controls available | As a document | |
| 69 | 6.1.3 | Communicate the necessary controls within the organization | In order to implement the controls determined in b) and c) | |
| 70 | 6.1.3 | Make the necessary controls available to stakeholders | As appropriate | |
| 71 | 6.1.3 | Retain a record on the AI risk treatment process | Cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
|
AI system impact assessment
|
|
|||
| 72 | 6.1.4 | Define and apply a process to assess the potential consequences on individuals, groups of individuals or society | That can result from the development, provision or use of AI systems | |
| 73 | 6.1.4 | Determine the potential consequences for individuals, groups of individuals or society | Resulting from the deployment, intended use, and foreseeable misuse of the AI system | |
| 74 | 6.1.4 | Take into account the specific technical and societal context | Where the AI system is deployed and applicable jurisdictions | |
| 75 | 6.1.4 | Document the result of the AI system impact assessment | Where appropriate, the result can be made available to relevant stakeholders | |
| 76 | 6.1.4 | Consider the results of the AI system impact assessment in the risk assessment | Cf. 6.1.2. Annex A.5 provides controls for assessing the impact of the AI system | |
|
6.2
|
Objectives
|
|||
| 77 | 6.2 | Establish AI objectives | For all functions and levels in the organization | |
| 78 | 6.2 a | Determine AI objectives | Consistent with the AI policy | |
| 79 | 6.2 b | Determine AI objectives | Measurable, if practicable | |
| 80 | 6.2 c | Determine AI objectives | Taking into account the applicable requirements to AI, the results of the risk assessment and treatment | |
| 81 | 6.2 d | Monitor AI objectives | Cf. sub-clause 9.1 | |
| 82 | 6.2 e | Communicate AI objectives | Cf. sub-clause 7.4 | |
| 83 | 6.2 f | Update AI objectives | As appropriate | |
| 84 | 6.2 g | Make available AI objectives | And retain them as documents, cf. sub-clause 7.5 | |
| 85 | 6.2 | Determine what will be done | When planning how to achieve its AI objectives | |
| 86 | 6.2 | Determine what resources will be required | When planning how to achieve its AI objectives | |
| 87 | 6.2 | Determine who will be responsible | When planning how to achieve its AI objectives | |
| 88 | 6.2 | Determine when it will be completed | When planning how to achieve its AI objectives | |
| 89 | 6.2 | Determine how the results will be evaluated | When planning how to achieve its AI objectives | |
|
Planning of changes
|
|
|||
| 90 | 6.3 | Carry out the changes of the AIMS in a planned manner | Before applying them | |
|
7
|
Support
|
|||
|
7.1
|
Resources
|
|||
|
91
|
7.1
|
Identify and provide the resources needed | In order to establish, apply, maintain and improve the AIMS | |
|
7.2
|
Competence
|
|
||
| 92 | 7.2 | Determine the necessary competence of the people involved |
Those involved can affect AI performance |
|
| 93 | 7.2 | Ensure that these people are competent | On the basis of initial and professional training and experience | |
| 94 | 7.2 | Take actions to acquire and keep the necessary competence updated | And evaluate the effectiveness of these actions. Actions include training, but also supervision, reassignment and recruitment of competent people | |
| 95 | 7.2 | Make available records on competence | Cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
|
7.3
|
Awareness
|
|
||
|
96
|
7.3
|
Make people aware of the AI policy | Cf. sub-clause 5.2 | |
| 97 | 7.3 | Make people aware of the importance of their contribution to the effectiveness of the AIMS | And the beneficial effects of improved performance of the AIMS | |
| 98 | 7.3 | Make people aware of the repercussions and consequences of not conforming with AIMS requirements | Do not forget the potential consequences on all professional activities | |
|
7.4
|
Communication
|
|||
| 99 | 7.4 | Determine internal and external communication needs | Including on which subjects, cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
| 100 | 7.4 | Determine internal and external communication needs | Including when to communicate | |
| 101 | 7.4 | Determine internal and external communication needs | Including with whom to communicate | |
| 102 | 7.4 | Determine internal and external communication needs | Including how to communicate | |
|
7.5
|
Documentation
|
|||
|
7.5.1
|
General
|
|
||
| 103 | 7.5.1 a | Include in the AIMS the documentation required by ISO 42001 |
Documents (documented information) available, to retain, to identify, to control:
Policy:
|
|
| 104 | 7.5.1 b | Include documentation deemed necessary for the effectiveness of the AIMS |
This documentation is specific in relation to the size of the organization, to the scope, to the complexity of the processes and their interactions to the competence of the personnel |
|
|
7.5.2
|
Creating and updating
|
|||
| 105 | 7.5.2 | Identify and describe the documentation appropriately | When creating and updating. As title, author, date, codification | |
| 106 | 7.5.2 | Ensure that the format and media of the documentation is appropriate | Examples of formats: language, software version and graphics. Examples of media: paper, electronic | |
| 107 | 7.5.2 | Review and validate documentation appropriately | In order to determine their relevance and suitability | |
|
7.5.3
|
Document control
|
|||
| 108 | 7.5.3 a | Control documents so that they are available and suitable for use | When and where needed. According to the requirements of the AIMS and the ISO 42001 standard | |
| 109 | 7.5.3 b | Control documentation so that it is properly protected | As loss of confidentiality, improper use or loss of integrity | |
| 110 | 7.5.3 | Apply distribution, access, retrieval and usage activities | In order to control the documentation | |
| 110 | 7.5.3 | Apply storage and preservation activities | Including legibility preservation | |
| 112 | 7.5.3 | Apply change control activities | Like version control | |
| 113 | 7.5.3 | Apply retention and disposition activities | By determining for each document the retention period and the way of disposal | |
| 114 | 7.5.3 | Identify and control documents of external origin | List of documentation deemed necessary for the planning and operation of the AIMS, including that of external origin | |
|
8
|
Operation
|
Do | ||
|
8.1
|
Planning and control
|
|||
| 115 |
8.1 | Plan, apply, control and maintain the processes necessary to meet the requirements of the AIMS | By establishing criteria for these processes and carrying out specific actions in the sub-clause 6.1 | |
| 116 | 8.1 | Plan, apply, control and maintain the processes necessary to meet the requirements of the AIMS | By implementing control of these processes | |
| 117 | 8.1 | Implement controls related to the AI management system | According to 6.1.3, as with the development of the AI system, life cycle-related usage controls | |
| 118 | 8.1 | Monitor the effectiveness of these controls | By taking actions to limit any negative impact. Cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
| 119 | 8.1 | Take into account corrective actions | To ensure that the processes are carried out as planned. Cf. paragraph 7.5.1 | |
| 120 | 8.1 | Make sufficient documents available | To ensure that the processes are carried out as planned. Cf. paragraph 7.5.1 | |
| 121 | 8.1 | Control planned changes and analyze unforeseen ones | By taking action to limit any negative impact. Cf. paragraph 7.5.1 | |
| 122 | 8.1 | Ensure that outsourced processes are controlled and relevant | Including outsourced products and services | |
|
AI risk assessment
|
|
|||
| 123 | 8.2 | Perform AI risk assessments regularly | Or when significant changes are proposed or occur | |
| 124 | 8.2 | Retain records of the results of all AI risk assessments | Results of risk assessment, cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
|
AI risk treatment
|
|
|||
| 125 | 8.3 | Apply the risk treatment plan | According to 6.1.3, and verify the effectiveness of the plan | |
| 126 | 8.3 | Perform a risk treatment process | For any new risk identified in accordance with 6.1.3 | |
| 127 | 8.3 | Review and revalidate risk treatment options | For risk treatment options that are not effective in accordance with 6.1.3 | |
| 128 | 8.3 | Update the risk treatment plan | For risk treatment options that are not effective in accordance with 6.1.3 | |
| 129 | 8.3 | Retain records on the results of all AI risk treatments | Risk treatment plan, cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
|
8.4
|
AI system impact assessment
|
|||
| 130 | 8.4 | Perform AI system impact assessments | According to 6.1.4 at planned intervals or following significant changes | |
| 131 | 8.4 | Retain records of the results of all AI system impact assessments | Risk treatment plan, cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
|
9
|
Performance
|
|||
|
Inspection
|
||||
| 132 | 9.1 | Determine what to inspect (monitor and measure) | Including AI processes and measures to achieve objectives | |
| 133 | 9.1 | Determine inspection methods | Including analysis and evaluation to ensure the validity of the results. Any valid result is comparable and reproducible | |
| 134 | 9.1 | Determine when to inspect | Including the points where monitoring and measurement are carried out | |
| 135 | 9.1 | Determine when to analyze inspection results | Including the moment of evaluation of the results | |
| 136 | 9.1 | Make available the results of inspection | As records, cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
| 137 | 9.1 | Evaluate the performance of the AIMS | Including the effectiveness of the AIMS | |
|
Internal audit
|
|
|||
|
9.2.1
|
General
|
|
||
| 138 | 9.2.1 a 1 | Perform internal audits at scheduled intervals to provide information to determine whether the AIMS meets organizational requirements | Including policy and objectives, cf. sub-clauses 5.2 and 6.2 | |
| 139 | 9.2.1 a 2 | Perform internal audits at scheduled intervals to provide information to determine whether the AIMS meets ISO 42001 requirements | Requirements in clauses 4 to 10 and Anne A of the standard | |
| 140 | 9.2.1 b | Perform internal audits at scheduled intervals to verify whether the AIMS is effectively implemented | And maintained. Cf. management review, sub-clause 9.3 | |
|
9.2.2
|
Internal audit program
|
|
||
| 141 | 9.2.2 | Plan, establish, apply and maintain the audit program | Including frequency, methods, responsibilities, planning and reporting requirements. Follow the recommendations of ISO 19011 | |
| 142 | 9.2.2 | Take into account in the audit program the importance of the processes | And results of previous audits | |
| 143 | 9.2.2 a | Define the audit criteria | And the scope of each audit. Follow the recommendations of ISO 19011 | |
| 144 | 9.2.2 b | Select auditors | In order to carry out objective and impartial audits. Follow the recommendations of ISO 19011 | |
| 145 | 9.2.2 c | Report the results of the audits | To the direction concerned | |
| 146 | 9.2.2 | Make available as record the application of the audit program | And audit results, cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
|
Management review
|
||||
|
9.3.1
|
General
|
|
||
| 147 | 9.3.1 | Review the AIMS at scheduled intervals | To ensure that the AIMS is still appropriate, adequate and effective. "No system is perfect" | |
|
9.3.2
|
Management review inputs
|
|
||
| 148 | 9.3.2 a | Take into consideration the progress of actions decided during the previous management review | Use the latest management review report | |
| 149 | 9.3.2 b | Take into consideration the modifications of the relevant issues for the AIMS | Cf. sub-clause 4.1 | |
| 150 | 9.3.2 c | Include changes to stakeholder requirements (needs and expectations) | Cf. sub-clause 4.2 | |
| 151 | 9.3.2 d 1 | Consider feedback trends |
Including nonconformities and corrective actions, cf. sub-clause 10.2 |
|
| 152 | 9.3.2 d 2 | Consider trends in inspection results | In other words, the results of monitoring and measurement, cf. sub-clause 9.1 | |
| 153 | 9.3.2 d 3 | Consider trends in audit results |
Cf. sub-clause 9.2 |
|
| 154 | 9.3.2 e | Consider opportunities for continual improvement | Cf. sub-clause 10.1 | |
|
9.3.3
|
Management review results
|
|
||
| 155 | 9.3.3 | Include continual improvement decisions in the results of the management review | And any changes to the AIMS, cf. sub-clause 10.2 | |
| 156 | 9.3.3 | Make available a record on the conclusions of the management review | As evidence. Cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
|
10
|
Improvement
|
|||
|
10.1
|
Continual improvement
|
|||
| 157 | 10.1 |
Continually improve the suitability, adequacy and effectiveness of the AIMS
|
By improving overall performance | |
|
Nonconformity and corrective action
|
|
|||
| 158 | 10.2 a 1 | React to the nonconformity | In order to control and correct it | |
| 159 | 10.2 a 2 |
React to the nonconformity |
In order to deal with the consequences of nonconformity | |
| 160 | 10.2 b 1 |
Review the nonconformity |
Evaluate whether action is needed to eliminate the cause | |
| 161 | 10.2 b 2 | Find the cause of the nonconformity | If possible the root cause | |
| 162 | 10.2 b 3 | Find out if similar nonconformities have occurred | Or could occur | |
| 163 | 10.2 c | Implement any action needed | Including corrective actions | |
| 164 | 10.2 d | Review the effectiveness of any undertaken action | Including any corrective action | |
| 165 | 10.2 e | Make changes to the AIMS | If necessary | |
| 166 | 10.2 | Take corrective actions appropriate to actual or potential consequences | In relation to the nonconformities that appeared | |
| 167 | 10.2 | Make available a record on the nature of nonconformities | Cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
| 168 | 10.2 | Make available a record on the results of corrective actions | Cf. sub-clause 7.5.1 | |
|
Annex A (normative)
|
||||
|
Policies related to AI
|
||||
| 169 | A.2.2 | Document a policy for the development or use of AI systems | Cf. sub-clause 5.2 | |
| 170 | A.2.3 | Determine in which cases other policies can be affected by or apply to, the organization's objectives | With respect to AI systems | |
| 171 | A.2.4 | Review at planned intervals the AI policy | In order to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy and effectiveness | |
|
Internal organization
|
|
|||
| 172 | A.3.2 | Define and allocate roles and responsibilities | According to the needs of the organization | |
| 173 | A.3.3 | Define and put in place a process to report concerns | With respect to an AI system throughout its life cycle | |
|
Resources for AI systems
|
|
|||
| 174 | A.4.2 | Identify and document relevant resources | Required for the activities at given AI system life cycle stages | |
| 175 | A.4.3 | Document information about the data resources | Utilized for the AI system | |
| 176 | A.4.4 | Document information about the tooling resources | Utilized for the AI system | |
| 177 | A.4.5 | Document information about the system and computing resources | Utilized for the AI system | |
| 178 | A.4.6 | Document information about the human resources and their competence | Utilized for the development, deployment, operation, change management, maintenance, transfer and decommissioning, as well as verification and integration of the AI system | |
|
Assessing impacts of AI systems
|
|
|||
| 179 | A.5.2 | Establish a process to assess the potential consequences for individuals, groups of individuals or societies | That can result from the AI system throughout its life cycle | |
| 180 | A.5.3 | Document the results of AI system impact assessments | And retain results for a defined period | |
| 181 | A.5.4 | Assess and document the potential impacts of AI systems | To individuals or groups of individuals | |
| 182 | A.5.5 | Assess and document the potential societal impacts of their AI systems | Throughout its life cycle | |
|
AI system life cycle
|
||||
|
Management guidance for AI system development
|
|
|||
| 183 | A.6.1.2 | Identify and document objectives to guide the responsible development of AI systems | And take those objectives into account and integrate measures to achieve them in the development life cycle | |
| 184 | A.6.1.3 | Define and document the specific processes | For the responsible design and development of the AI system | |
|
AI system life cycle
|
|
|||
| 185 | A.6.2.2 | Specify and document requirements for new AI systems | Or material enhancements to existing systems | |
| 186 | A.6.2.3 | Document the AI system design and development | Based on organizational objectives, documented requirements and specification criteria | |
| 187 | A.6.2.4 | Define and document verification and validation measures for the AI system | And specify criteria for their use | |
| 188 | A.6.2.5 | Document a deployment plan | And ensure that appropriate requirements are met prior to deployment | |
| 189 | A.6.2.6 | Define and document the necessary elements for the ongoing operation of the AI system | Include system and performance monitoring, repairs, updates and support | |
| 190 | A.6.2.7 | Determine what AI system technical documentation is needed for each relevant category of interested parties | Such as users, partners, supervisory authorities, and provide the technical documentation to them in the appropriate form | |
| 191 | A.6.2.8 | Determine at which phases of the AI system life cycle event logs should be enabled | At the minimum when the AI system is in use | |
|
Data for AI systems
|
|
|||
| 192 | A.7.2 | Define, document and implement data management processes | Related to the development of AI systems | |
| 193 | A.7.3 | Determine and document details about the acquisition and selection of the data | Used in AI systems | |
| 194 | A.7.4 | Define and document requirements for data quality | And ensure that data used to develop and operate the AI system meet those requirements | |
| 195 | A.7.5 | Define and document a process for recording the provenance of data used in its AI systems | Over the life cycles of the data and the AI system | |
| 196 | A.7.6 | Define and document its criteria for selecting data preparations | And the data preparation methods to be used | |
|
Information for interested parties of AI systems
|
||||
| 197 | A.8.2 | Determine and provide the necessary information | To users of the AI system | |
| 198 | A.8.3 | Provide capabilities for interested parties to report adverse impacts | Of the AI system | |
| 199 | A.8.4 | Determine and document a plan for communicating incidents | To users of the AI system | |
| 200 | A.8.5 | Determine and document their obligations to reporting information about the AI system | To interested parties | |
|
Use of AI systems
|
|
|||
| 201 | A.9.2 | Define and document the processes | For the responsible use of AI systems | |
| 202 | A.9.3 | Identify and document objectives | To guide the responsible use of AI systems | |
| 203 | A.9.4 | Ensure that the AI system is used according to the intended uses of the AI system | And its accompanying documentation | |
|
Third-party and customer relationships
|
|
|||
| 204 | A.10.2 | Ensure that responsibilities within their AI system life cycle are allocated between the organization | And its partners, suppliers, customers and third parties | |
| 205 | A.10.3 | Establish a process to ensure that its usage of services, products or materials provided by suppliers aligns with the organization’s approach | To the responsible development and use of AI systems | |
| 206 | A.10.4 | Ensure that its responsible approach to the development and use of AI systems considers their customer expectations | And customer needs | |
|
|
|
|
||




